🏢 1. Introduction – Why Troubleshooting Skills Save Time & Money
When a 6–10 ton commercial packaged unit stops doing its job, your building notices—fast.
-
Tenants complain.
-
Utility bills spike.
-
In extreme weather, operations can grind to a halt.
Having basic troubleshooting knowledge:
-
Cuts down on unnecessary service calls.
-
Helps you relay accurate info to HVAC pros.
-
Lets you fix small problems in-house before they snowball.
That said—troubleshooting a large packaged unit is not about guessing. It’s about safe, methodical testing.
⚠ 2. Safety First
Before touching the unit:
-
Lockout/Tagout (LOTO): Shut off and lock power at the disconnect. Attach a tag so no one flips it back on.
-
Wear PPE: Gloves, safety glasses, and in some cases fall protection for rooftop units.
-
Refrigerant Safety: Use gauges rated for the refrigerant type (R-410A, R-454B, etc.). Avoid venting refrigerant—it’s both illegal and dangerous.
-
Gas Safety: For furnace-equipped units, shut off gas at the supply valve before working on combustion components.
Jake’s rule: If you’re not licensed for gas or refrigerant work, limit yourself to inspections and basic fixes.
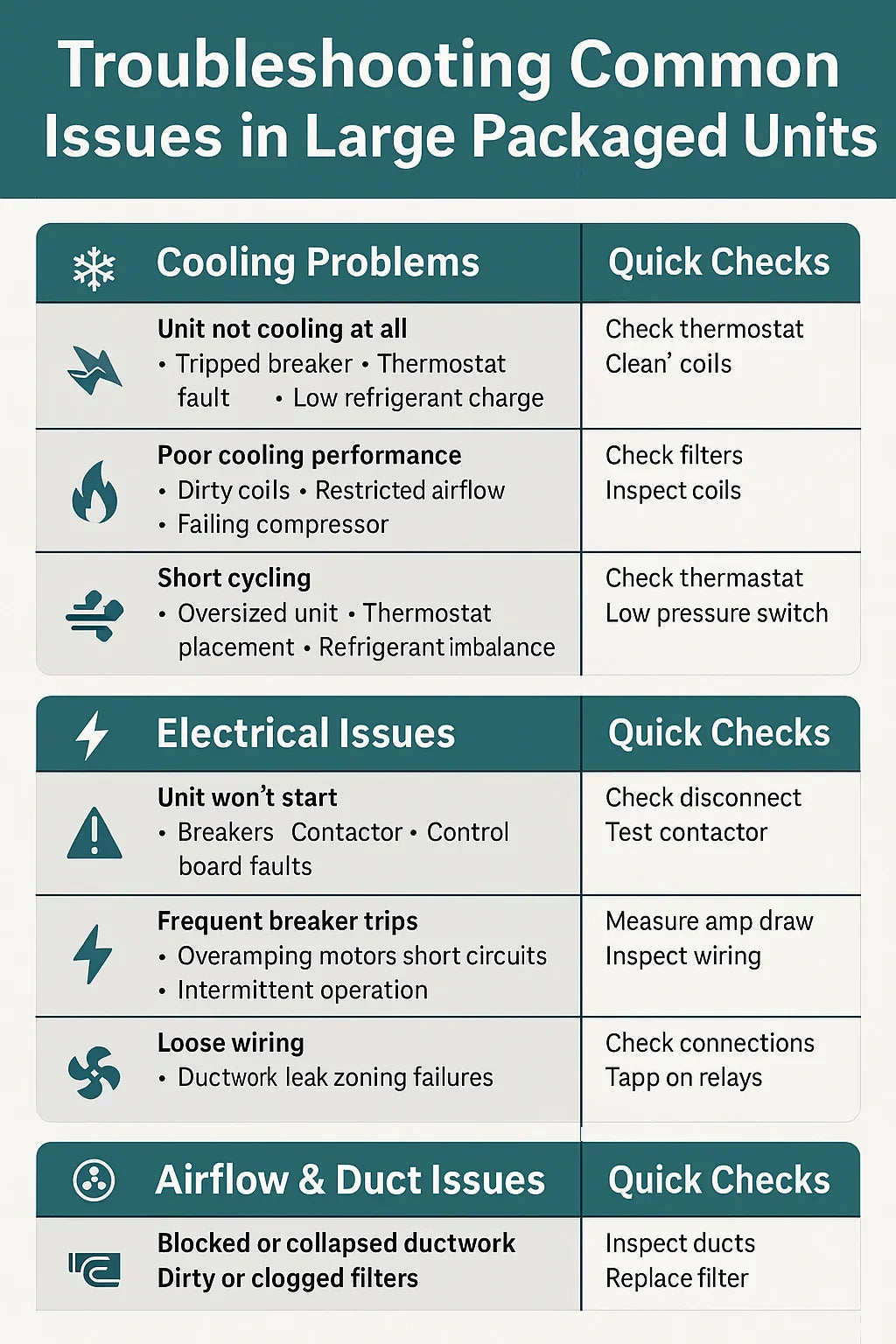
❄ 3. Cooling Problems
A. Unit Not Cooling At All
Likely Causes:
-
Tripped circuit breaker
-
Blown control fuse
-
Thermostat not calling for cooling
-
Contactor not engaging
-
Low-pressure switch open due to refrigerant loss
Steps:
-
Check thermostat mode and setpoint.
-
Inspect breaker/fuses.
-
Listen for contactor pull-in.
-
If contactor is engaged but compressor/fan aren’t running—check capacitor and motor.
B. Poor Cooling Performance
Likely Causes:
-
Dirty condenser coils
-
Clogged air filter
-
Low refrigerant charge
-
Worn compressor
-
Economizer damper stuck open
Steps:
-
Inspect coils for dirt/debris—clean if needed.
-
Replace air filter.
-
Check superheat/subcooling against manufacturer specs.
-
Inspect economizer operation.
C. Short Cycling (Cooling)
Likely Causes:
-
Oversized unit
-
Thermostat placed in poor location
-
Refrigerant imbalance
-
Faulty low-pressure control
Steps:
-
Observe cycle length—should be several minutes, not seconds.
-
Check thermostat placement (avoid drafts/heat sources).
-
Verify refrigerant pressures.
🔥 4. Heating Problems (Gas Furnace Models)
A. No Heat
Likely Causes:
-
Igniter failure
-
No gas supply (closed valve, empty tank)
-
Limit switch open
-
Faulty flame sensor
Steps:
-
Confirm gas valve is open.
-
Reset limit switch if tripped.
-
Test igniter resistance.
-
Clean flame sensor with fine emery cloth.
B. Insufficient Heat
Likely Causes:
-
Dirty burners
-
Low gas pressure
-
Heat exchanger issues
-
Blocked vent
Steps:
-
Inspect burner flame (should be blue, steady).
-
Measure manifold pressure.
-
Check vent/flue for blockages.
C. Uneven Heating
Likely Causes:
-
Duct leaks
-
Zone damper failure
-
Blower belt slipping
Steps:
-
Inspect ducts for damage.
-
Test damper actuator operation.
-
Tighten/replace blower belt.
⚡ 5. Electrical Issues
A. Unit Won’t Start
Likely Causes:
-
Tripped breaker
-
Control transformer failure
-
Thermostat wiring fault
Steps:
-
Reset breaker (if it trips again, investigate short).
-
Measure transformer secondary voltage.
-
Check for 24V signal at contactor.
B. Frequent Breaker Trips
Likely Causes:
-
Overamping fan or compressor motor
-
Short circuit in wiring
-
Bad capacitor causing hard starts
Steps:
-
Measure amp draw on each motor.
-
Inspect wiring insulation.
-
Test capacitors with meter.
C. Intermittent Operation
Likely Causes:
-
Loose wire connections
-
Failing relays
-
Faulty control board
Steps:
-
Tighten all terminal screws.
-
Tap suspect relays—if operation changes, replace.
-
Look for burn marks on board.
🌬 6. Airflow & Duct Issues
Common Symptoms: Low airflow, uneven temperatures, noise in ducts.
Likely Causes:
-
Collapsed or blocked ductwork
-
Dirty filter
-
Blower motor failure
-
Belt misalignment
Steps:
-
Check filter.
-
Measure static pressure.
-
Inspect ducts for obstructions.
-
Verify blower speed setting.
💧 7. Water & Drainage Problems
A. Water Overflow Inside Building
-
Clogged condensate drain line
-
Missing or broken trap
-
Rusted drain pan
Steps:
-
Clear drain line with nitrogen or vacuum pump.
-
Verify trap is installed and functional.
-
Replace damaged pans.
B. Frozen Evaporator Coils
-
Low airflow (dirty filter, blower issue)
-
Low refrigerant charge
Steps:
-
Inspect and correct airflow issues.
-
Check refrigerant pressures.
📑 8. Creating a Troubleshooting Log
Why it matters:
-
Helps track recurring faults.
-
Makes vendor service faster & cheaper.
-
Provides data for capital planning.
Log Template:
-
Date/time
-
Symptom description
-
Steps taken/tests performed
-
Results & readings
-
Resolution or next action
🛠 9. Jake’s Pro Troubleshooting Tips
-
Start Simple: Check the obvious before diving deep.
-
Spare Parts: Keep fuses, belts, and filters in stock.
-
Know Your Unit: Learn the model-specific fault codes.
-
Document Everything: Today’s “minor issue” could be tomorrow’s “big problem” with a history.
-
Seasonal Awareness: Summer issues often tie to cooling, winter to heating—adjust your initial checks accordingly.
In the next topic we will know more about: How Long Do Commercial Packaged AC & Gas Furnace Units Last? Lifespan & Replacement Signs