If you’ve been researching new HVAC systems, you’ve probably seen SEER2 ratings listed on EnergyGuide labels and in product descriptions. These numbers are designed to help you compare efficiency and make smart choices. But here’s the question homeowners often ask: do these ratings hold up in the real world—or are they inflated by ideal lab conditions?
The truth is, while SEER2 standards are more realistic than the old SEER testing, they’re still based on controlled conditions that may not perfectly reflect your home. In this guide, I’ll break down how SEER2 testing works, why lab conditions matter, and what you should watch for to make sure your system delivers the savings and comfort you expect.
How SEER2 Testing Works
SEER2, short for Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio 2, replaced SEER in 2023. The goal was to update testing so it reflects real-world static pressure and airflow conditions better than the old method.
-
Static pressure: SEER2 tests equipment under higher external static pressure to mimic duct resistance.
-
Temperature ranges: Units are tested within controlled indoor and outdoor conditions.
-
Standardized ducts: Ducted systems are tested with specified setups to ensure consistency.
These changes were mandated under the AHRI 2023 energy efficiency standards, making SEER2 ratings more representative than SEER. But even so, your home isn’t a lab—and that’s where differences show up.
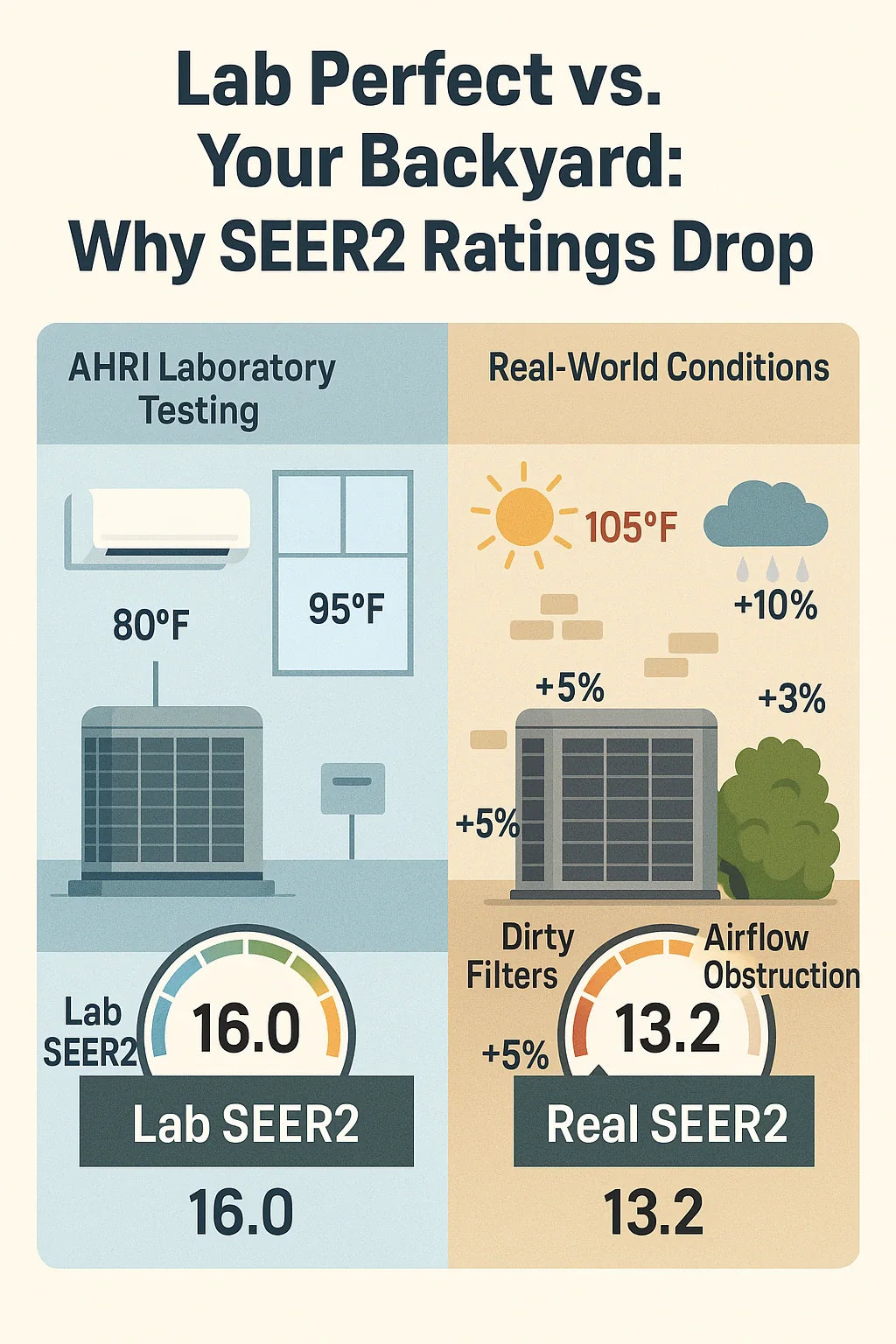
Why Lab Conditions Don’t Always Match Real-World Use
Even with SEER2 improvements, lab-tested efficiency can differ from what homeowners see in daily operation. Here are the biggest reasons why.
Ductwork Losses
SEER2 tests account for static pressure but can’t replicate leaky, poorly insulated, or undersized ducts in many homes. If your ducts are in an attic or crawlspace, losses may be 20–30% higher than the test assumes.
The DOE duct performance guidance highlights how sealing and insulating ducts can recover lost efficiency and bring performance closer to rated SEER2.
Climate Variability
Testing uses standardized conditions, but climates across the U.S. vary dramatically. A system in Phoenix, AZ, faces far more cooling hours than one in Portland, OR. That difference affects both energy savings and payback.
The EIA Climate Zones dataset maps these differences, showing why efficiency ratings need to be understood through the lens of your region.
Occupant Behavior
How you set and use your thermostat matters as much as the system itself. Running your AC at 68°F all summer will undermine even the most efficient unit.
The ENERGY STAR thermostat efficiency guidance shows how programmable and smart thermostats help homeowners achieve rated efficiency by aligning use with actual needs.
Installation Quality
No lab test can account for a poor installation. Oversized systems, unbalanced ductwork, or refrigerant charge errors can drop performance significantly.
The ACCA quality installation resources stress proper design (Manual J load calculations) and commissioning to protect efficiency.
Signs Your SEER2 Rating May Not Match Reality
If your system’s lab rating seems out of sync with your utility bills or comfort, you might be dealing with a gap between rated and real-world performance. Watch for these signs:
-
Higher-than-expected bills despite a high-SEER2 system.
-
Uneven comfort across rooms, especially in multi-story homes.
-
Short cycling or long run times, indicating poor sizing or airflow.
-
Monitoring tools (smart thermostats, energy apps) showing usage inconsistent with SEER2 expectations.
How to Protect Yourself from Inflated Expectations
Homeowners can’t change how lab tests are conducted, but you can take steps to keep your system’s real-world efficiency as close to SEER2 as possible.
Ask for a Manual J Load Calculation
Proper sizing is crucial. Too large or too small, and your system won’t deliver its rated efficiency.
Insist on Professional Duct Testing
Have your contractor measure duct leakage and static pressure. Sealing and insulating ducts is often the most cost-effective upgrade for efficiency.
Use Smart Tools to Track Energy Use
Many systems and thermostats now provide energy reports. Compare your kWh consumption against past bills to see if your SEER2 system is performing as promised.
Schedule Regular Maintenance
Filters, coils, and refrigerant levels all impact efficiency. Seasonal checkups are essential to close the gap between lab-tested ratings and real-world performance.
Final Thoughts from Alex Lane
So, are SEER2 ratings inflated by ideal lab conditions? Not exactly—but they do present a best-case scenario. Think of SEER2 as a useful benchmark, not a guaranteed outcome.
By sealing ducts, monitoring usage, and keeping up with maintenance, you can bring your system’s performance much closer to what the label promises.
Want to understand SEER2 from the ground up? Start with What is SEER2 and Why It Matters.
Since this is the final cluster in the series, circle back to the beginning and read SEER2 vs. SEER: What’s Changed and Why It Matters to reinforce your foundation.
Alex Lane
Your Home Comfort Advocate