By Alex Lane | Your Home Comfort Advocate
When you're upgrading your HVAC system, one of the most important numbers you'll see is the efficiency rating — and lately, that number might look different. That’s because starting in 2023, the industry transitioned from the long-used SEER rating system to a new standard: SEER2.
But what’s the difference? And more importantly, why should you care?
This guide breaks it down in plain English, so you can understand how these changes impact your wallet, your comfort, and your next HVAC investment.
🔧 What is SEER?
SEER stands for Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio. It measures how efficiently a cooling system (like a central air conditioner or heat pump in cooling mode) operates over an average cooling season. The higher the SEER, the more efficient the unit.
The formula is simple:
SEER = Total Cooling Output (BTUs) / Total Energy Used (Watt-hours)
For years, SEER ratings helped homeowners gauge efficiency — but they were tested in ideal lab conditions, not the ductwork-restricted, filter-clogged world of real homes.
That’s where SEER2 comes in.
🔁 What is SEER2?
SEER2, or Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio 2, is the updated standard developed by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE). It reflects the same basic idea — measuring cooling efficiency — but the testing procedures have changed to better reflect how HVAC systems perform in real life.
Key difference? SEER2 simulates real-world conditions by increasing external static pressure in the test — essentially mimicking how airflow is restricted in actual homes due to ductwork and filters.
This updated procedure is part of the DOE’s M1 testing protocol, which replaced the older M standard in 2023.
For a technical deep dive, check out the SEER2 Overview from SEER2.com.
🔍 SEER vs. SEER2: Side-by-Side Comparison
| Category | SEER (Old Standard) | SEER2 (New Standard) |
|---|---|---|
| Testing Conditions | Ideal lab airflow (0.1" WC) | Real-world airflow (0.5" WC) |
| Procedure | DOE M Test Procedure | DOE M1 Test Procedure |
| Rating Outcome | Slightly inflated | 4–5% lower, but more realistic |
| Effective Date | Until Dec 31, 2022 | Jan 1, 2023 onward |
| Realism | Lower | Much higher |
To put it simply: SEER2 is SEER — but honest.
💡 Why SEER2 Replaced SEER
1. Realistic Performance Metrics
Older SEER ratings often made HVAC systems appear more efficient than they’d actually be in your home. SEER2 corrects for that with real-life duct conditions.
2. Clearer Comparisons
Now that all new systems are rated using SEER2, you’re comparing apples to apples. This levels the playing field and empowers homeowners to choose smarter.
3. Aligned With New Efficiency Requirements
SEER2 is now part of the minimum federal and regional efficiency standards for 2025. If your system doesn’t meet SEER2 benchmarks, it may not be legally installed — or qualify for incentives.
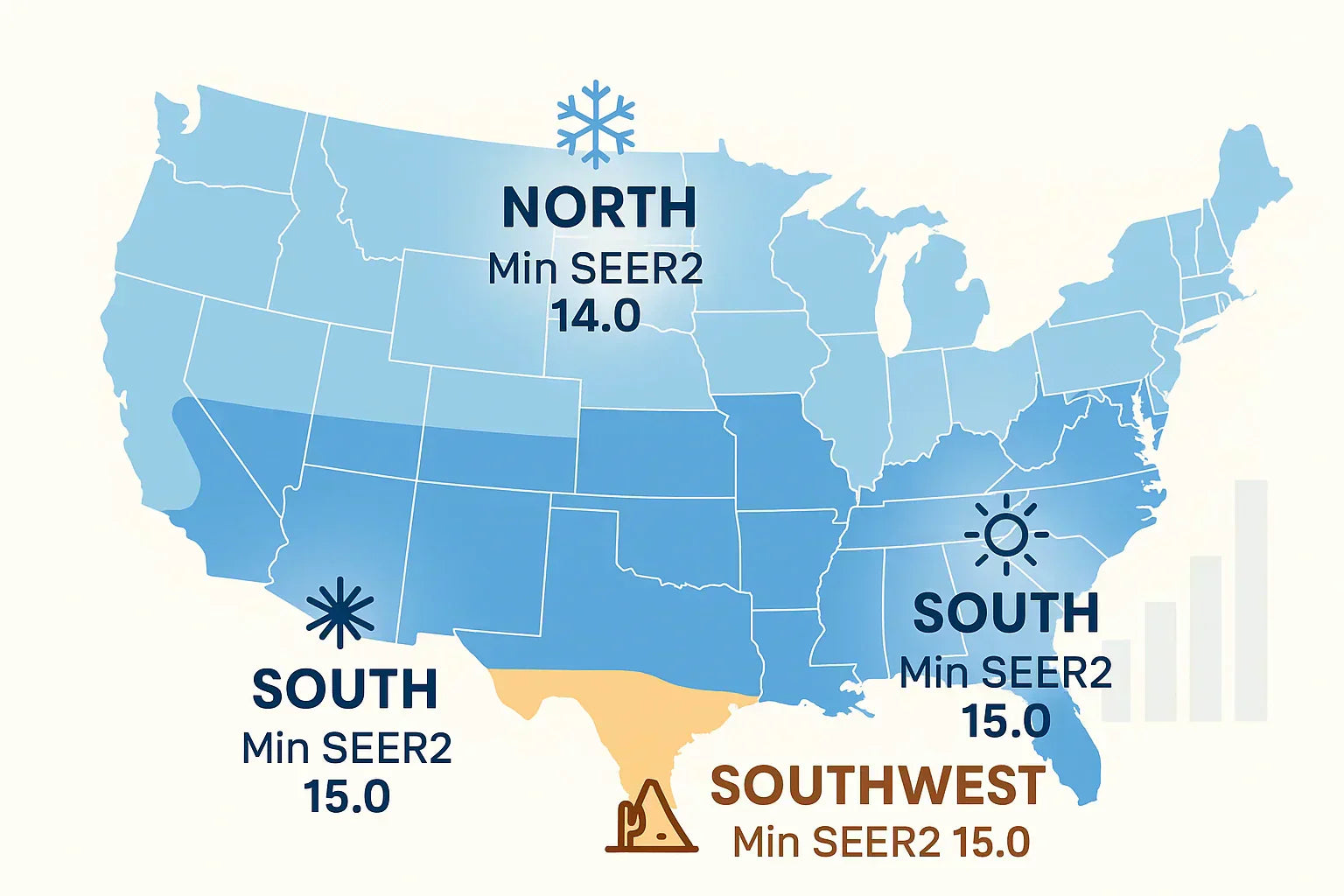
🌎 Regional Standards: SEER vs. SEER2 Minimums
Here’s a quick look at how SEER2 minimums compare to the old SEER standards:
| Region | SEER Minimum | SEER2 Minimum (2025) |
|---|---|---|
| North | 13.0 | 13.4 |
| South | 14.0 | 14.3 |
| Southwest | 14.0 | 13.8 (≥45k BTU/hr units) |
Want more detail? Visit the interactive map and updates at SEER2.com.
📉 SEER vs. SEER2: Efficiency Translation
If you're looking at an older system with SEER ratings, here’s a quick estimate to understand how it might translate into SEER2:
SEER2 ≈ SEER × 0.95
So if a unit was rated at 16 SEER, it would likely rate at around 15.2 SEER2 under the new testing standard.
That might sound like a downgrade — but remember, this isn’t about changing the equipment. It’s about changing how we measure efficiency in the real world.
🔍 How to Verify a System’s Rating
When browsing equipment, make sure to:
-
Look for the yellow EnergyGuide label — it should say “SEER2” clearly.
-
Ask the installer or distributor for the AHRI Certificate.
-
Use the AHRI Certified Directory to confirm the exact model’s SEER2 rating and matched system performance.
🧠 Smart Buying Tip
Don’t just assume “16 SEER” is compliant. If it’s not labeled SEER2, it might be outdated inventory — or it may not qualify for rebates, especially in 2025.
Make sure to ask your HVAC professional directly, and request written confirmation that the unit meets current SEER2 minimums for your region.
You can also use tools like the ENERGY STAR upgrade calculator to compare costs and savings based on efficiency level.
📘 Learn More: What is SEER2?
This post is part of our SEER2 series. For a full breakdown of how SEER2 works, why it was introduced, and how it affects homeowners in 2025, check out our main guide:
👉 What is SEER2 and Why It Matters
📖 Next in the Series: Understanding the Label
Want to know how to spot SEER2 ratings on HVAC units, EnergyGuide labels, and AHRI certificates?
👉 How to Read and Compare SEER2 Ratings on HVAC Labels
Alex Lane
Your Home Comfort Advocate