If your furnace kicks on with a bang, hums like a freight train, or keeps you up at night with every cycle — you’re not alone. Operating noise is a key comfort factor, especially in smaller homes, bedrooms near mechanical rooms, or open-concept layouts.
So which furnace type runs quieter: gas or electric? The answer isn’t just about the fuel — it’s also about how the system is built, installed, and maintained. In this guide, we’ll compare gas vs. electric furnace noise levels, what causes the sounds you hear, and how to enjoy a quieter home all winter long.
Why Furnace Noise Levels Matter
A furnace doesn’t need to be loud to be powerful. In fact, quiet operation is often a sign of better engineering, smoother airflow, and proper maintenance.
Here’s why homeowners care about sound:
-
Comfort: Loud cycling can disturb sleep or work-from-home calls
-
Perception of quality: A noisy furnace may feel outdated or neglected
-
Early warning: Unusual noise can signal loose parts or upcoming failure
According to Ventech, reducing HVAC noise not only improves acoustic comfort — it also enhances how efficiently air is distributed throughout the home, especially when airflow is properly balanced and unobstructed.
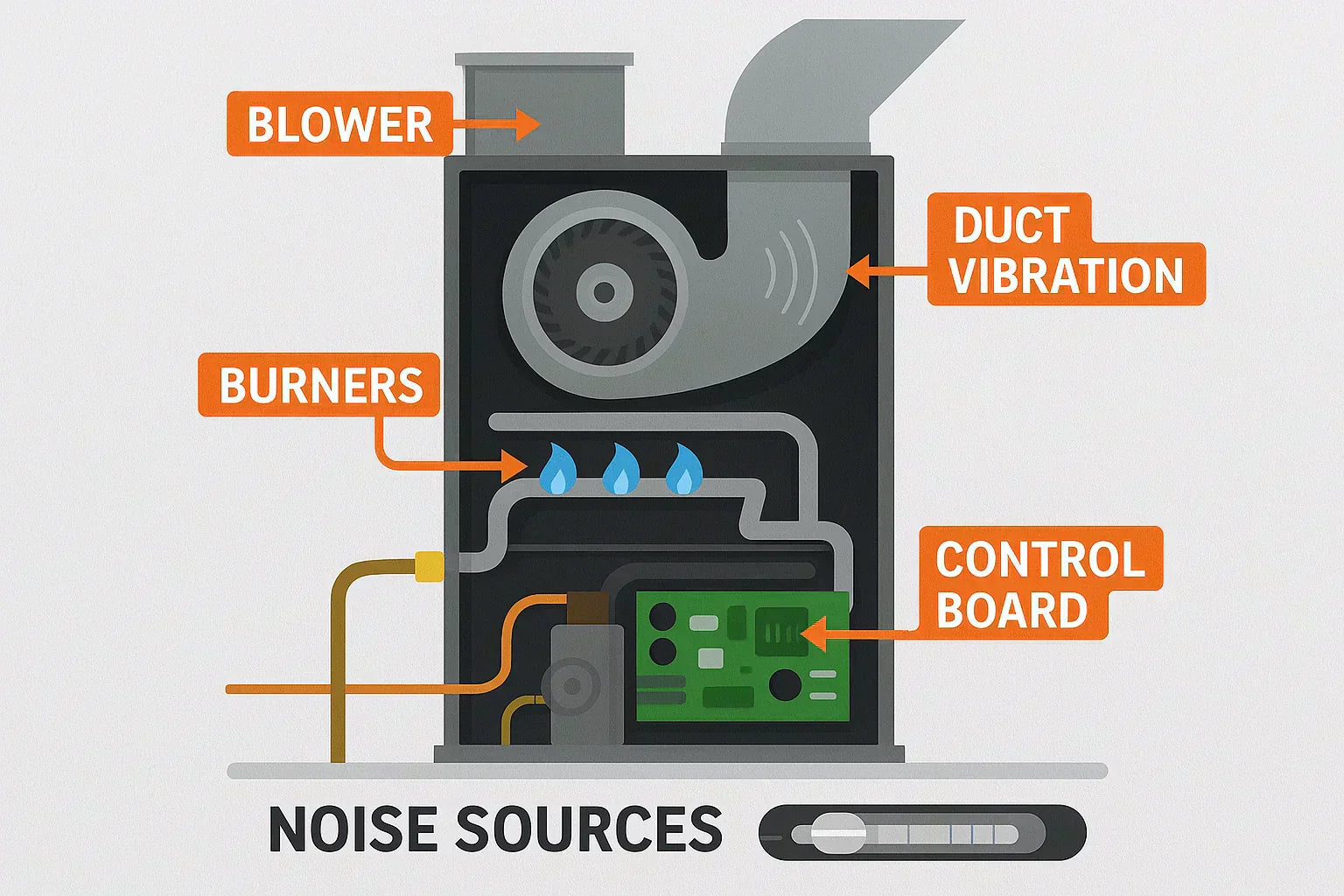
What Makes a Furnace Noisy?
Furnaces generate sound in several ways—some normal, some not.
Key Noise Sources
-
Blower fan: The biggest culprit for most systems. Oversized blowers or dirty fan blades can create roaring or rattling sounds.
-
Combustion burners (gas only): Clicking on startup, whooshing during ignition, or rumbling during shutdown.
-
Duct vibration: Poorly secured ductwork or high airflow can cause rattles or booms.
-
Electrical hum: Especially in electric models, relays or transformers may create low-frequency buzz.
According to Trane, persistent or unusual furnace noises — such as buzzing, humming, or rattling — may point to failing relays, loose wiring, or airflow problems. If the sound changes in volume or pattern, it’s best to investigate before a minor issue becomes a costly repair.
Typical Furnace Noise Levels (in Decibels)
| Furnace Type | Normal dB Range | Comparable Sound |
|---|---|---|
| Gas Furnace | 50–80 dB | Office chatter to vacuum cleaner |
| Electric Furnace | 40–70 dB | Quiet conversation to dishwasher |
| Heat Pump (for ref) | 40–60 dB | Library to refrigerator hum |
Electric systems tend to operate more quietly, but modern gas furnaces have improved dramatically—especially variable-speed models with soft start cycles.
Are Gas Furnaces Louder Than Electric?
Generally speaking, yes. But it depends on the model and how it’s installed.
Combustion Noise in Gas Systems
Gas furnaces ignite fuel using burners, which naturally introduces clicks, whooshes, or soft roaring sounds. In older systems, this can be abrupt and loud. You may also hear:
-
Gas valve engagement
-
Pilot or spark ignition
-
Flue gurgling during cold startup
According to Angi, some level of sound during ignition is expected, but loud bangs or booming noises may indicate delayed ignition, expanding ductwork, or venting issues — all of which can reduce efficiency and pose long-term risks if ignored.
Blower Operation
Older gas furnaces often use single-speed blower motors, which run at full blast or not at all. That sudden air rush adds to perceived noise.
Newer systems with variable-speed or ECM motors are much quieter.
Electric Furnace Noise Profile
Electric furnaces don’t burn fuel, so they naturally avoid combustion-related sounds. This gives them a leg up in most residential sound comparisons.
What You Might Hear
-
Low hum from heating coils energizing
-
Relay clicks during staging
-
Airflow rush from blower fan, especially in undersized ducts
Because they generate heat through electric resistance rather than combustion, they run smoother—though not completely silent.
Less Vibration and No Exhaust Venting
Electric systems have fewer moving parts and no need for venting, reducing the number of sound-producing components. If noise is present, it’s usually related to blower size or installation—not the heating elements themselves.
Ways to Reduce Furnace Noise (Gas or Electric)
Regardless of type, you can quiet your system with a few smart upgrades:
✅ Upgrade to a Variable-Speed Blower
Modern ECM motors ramp up slowly and maintain airflow without abrupt starts. They’re much quieter than single-speed models.
✅ Add Vibration Isolation Pads
Install rubber or cork vibration isolators beneath the furnace to reduce mechanical noise traveling through floors or walls.
✅ Insulate Your Ductwork
Foam or fiberglass insulation can absorb airflow noise, reduce vibration, and even improve efficiency.
✅ Seal Loose Panels
Check for screws, sheet metal gaps, or flex duct clamps that may be rattling.
✅ Schedule Maintenance
A dirty blower wheel or clogged filter can force your system to work harder (and louder). Family Handyman recommends annual service and filter replacement every 1–3 months.
Quiet Furnace Models to Consider
If noise is a top priority, look for models specifically designed for low sound ratings:
🔇 Top Quiet Gas Furnaces
-
Lennox SLP99V: Marketed as one of the quietest
-
Carrier Infinity 98: Known for its variable-speed capabilities
-
Trane XC95m: Excellent noise control and zoning options
🔇 Top Quiet Electric Furnaces
-
Rheem Classic Electric Series
-
Goodman MBR Series with ECM blower
-
Any electric furnace paired with a smart thermostat for reduced runtime
Look for decibel ratings in manufacturer spec sheets—a sign that noise has been tested and engineered for.
Final Takeaway: Choose the Quiet That Suits Your Space
If you’re chasing silence, electric furnaces have a natural advantage—but that doesn’t mean gas systems are out of the running. Today’s modulating gas furnaces with variable-speed fans are quieter than ever.
That said, installation quality matters just as much as furnace type. An oversized system, poorly sealed ducts, or an unbalanced blower can turn even a premium unit into a noisy headache.
👉 Want to learn how furnace type affects cost, lifespan, and efficiency too? Start here:
Gas vs. Electric Furnaces: Which is Better?
👉 Next in the series:
Gas Line and Electrical Grid Considerations for Your Furnace Type
Alex Lane
Your Home Comfort Advocate