Replacing a furnace isn’t cheap. That’s why one of the first questions homeowners ask is: How long will this thing actually last? Whether you’re looking at a gas furnace or an electric one, understanding the expected lifespan and durability can help you make a smarter, longer-term investment.
In this guide, we’ll compare the average service life of gas vs. electric furnaces, what affects their durability, and how to extend their performance for as long as possible.
Why Furnace Lifespan Matters to Homeowners
Furnaces are major purchases. When choosing between gas and electric, you’re not just comparing energy costs—you’re also weighing how long the system will serve your home before needing a costly replacement.
Lifespan ties directly into:
-
Total cost of ownership
-
Ongoing maintenance needs
-
Resale value and buyer confidence
It’s also where many myths start circulating. Some homeowners think electric units “never die,” while others believe gas units are “built like tanks.” The truth is a bit more nuanced—and heavily influenced by how the system is installed and maintained.
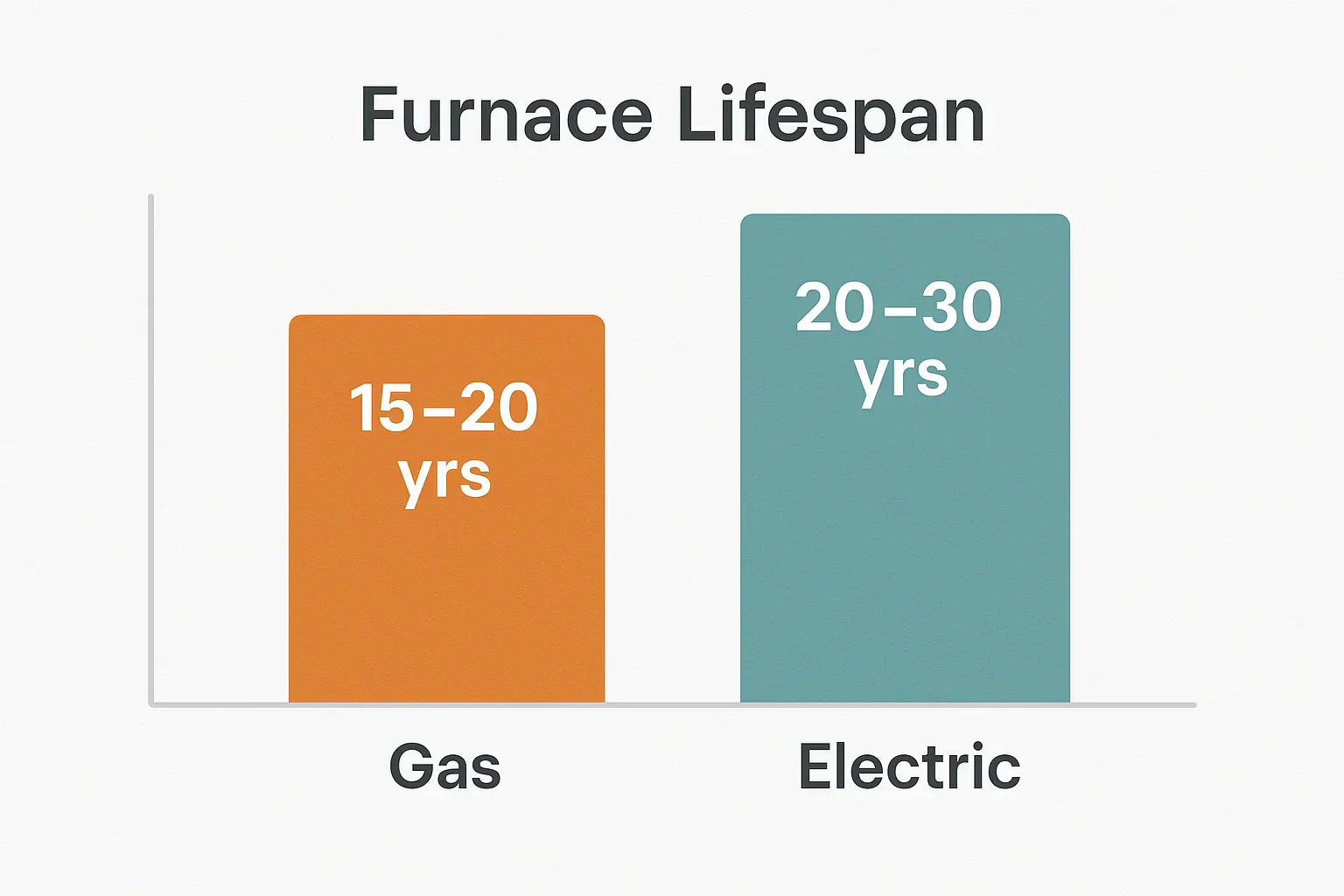
Average Lifespan of Gas Furnaces
Expected Range
A well-maintained gas furnace typically lasts 15 to 20 years. This range can vary based on factors like build quality, fuel type (natural gas vs. propane), and how often the system runs during the year.
Leading manufacturers like Carrier confirm this average, noting that lifespan can drop closer to 12–15 years in high-use regions with extreme winters.
Durability Factors
Gas furnaces undergo combustion every time they cycle on. That means they’re exposed to:
-
High heat stress on the heat exchanger
-
Moisture from venting, leading to corrosion
-
Wear on ignition components and blowers
Over time, these stress points can weaken parts and reduce overall system life—especially if the unit isn’t maintained regularly.
Common Failure Points
Some of the most frequent gas furnace breakdowns involve:
-
Cracked heat exchangers (which can be a safety hazard)
-
Failed ignition systems (spark igniter or hot surface igniter)
-
Worn blower motors or capacitors
According to Energy.gov, regular tune-ups and early part replacement can catch these issues before they lead to total system failure.
Average Lifespan of Electric Furnaces
Expected Range
Electric furnaces generally outlast gas models, with an average lifespan of 20 to 30 years, according to Angi. This longer lifespan is largely due to their simpler design and lack of combustion, which means:
-
Fewer moving parts
-
No burners or exhaust systems to corrode
-
Reduced exposure to high heat cycles
While they may have higher operating costs in some regions, electric furnaces often deliver more long-term reliability — especially when installed and maintained properly.
Durability Factors
Still, electric systems aren’t invincible. Their durability depends on:
-
Voltage stability — frequent power surges can fry relays or boards
-
Airflow and ductwork — undersized systems wear out faster
-
Indoor air quality — dust and moisture can reduce electrical component life
Routine filter changes and surge protection go a long way in protecting your investment.
Common Failure Points
While electric systems skip combustion-related issues, they’re still prone to:
-
Relay or sequencer failures
-
Heating element burnout (especially after decades of use)
-
Blown control boards from power surges
Still, these issues tend to be less expensive to repair than a cracked heat exchanger on a gas unit.
Maintenance Requirements Comparison
Gas furnaces require more intensive maintenance due to the combustion process. That includes:
-
Annual inspection of the burner and heat exchanger
-
Cleaning of flue pipes and vents
-
Testing for carbon monoxide leaks
In contrast, electric furnaces have simpler maintenance needs—usually limited to filter changes, visual checks, and occasional component replacement. But because they’re “low-maintenance,” many homeowners forget to service them at all, which can shorten their lifespan.
As Bob Vila explains, the key to furnace longevity is not skipping annual service, regardless of the fuel type.
Durability in Harsh Climates
Gas Furnaces in Cold Weather
In sub-zero climates, gas furnaces operate more frequently, which adds mechanical wear. Frost-prone areas can also cause condensation in vent pipes—accelerating rust.
Electric Furnaces in Cold Weather
Electric resistance heat isn’t as efficient in extreme cold. While it doesn’t corrode like gas systems, it may run longer to maintain set temperatures, stressing elements and wiring. A properly sized unit (or pairing with a heat pump) helps offset this.
Humidity and installation quality matter for both types. Poor duct sealing or damp basements can affect internal components and reduce lifespan.
How to Extend Furnace Life (Any Type)
Here’s how to protect your investment, no matter what type of furnace you own:
✅ Change filters regularly
Dirty filters make the blower work harder and reduce airflow—shortening lifespan.
✅ Schedule professional maintenance annually
A licensed tech can catch small problems before they snowball. According to HVAC.com, annual tune-ups can extend your system’s life by 3–5 years.
✅ Install a surge protector
Especially important for electric systems, where boards and relays can be damaged by lightning or power spikes.
✅ Use a smart thermostat
Smart thermostats can reduce unnecessary run time and optimize fan cycles—cutting down on mechanical wear and saving energy.
Final Verdict: Which Furnace Type Lasts Longer?
Let’s break it down:
| Feature | Gas Furnace | Electric Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Avg. Lifespan | 15–20 years | 20–30 years |
| Maintenance Needs | Higher | Lower |
| Common Failure Points | Heat exchanger, igniter | Relays, elements |
| Upfront Cost | Moderate | Slightly lower |
| Operating Cost | Lower (in gas regions) | Higher (in cold climates) |
✅ Electric furnaces tend to last longer and require less maintenance.
✅ Gas furnaces offer faster heating and lower fuel costs in many regions, but need more frequent care.
Your best choice depends on your climate, utility rates, and how long you plan to stay in the home.
👉 Want a full breakdown of system performance and savings? Start here:
Gas vs. Electric Furnaces: Which is Better?
👉 Next in the series:
Operating Noise: Which Furnace Runs Quieter?
Alex Lane
Your Home Comfort Advocate