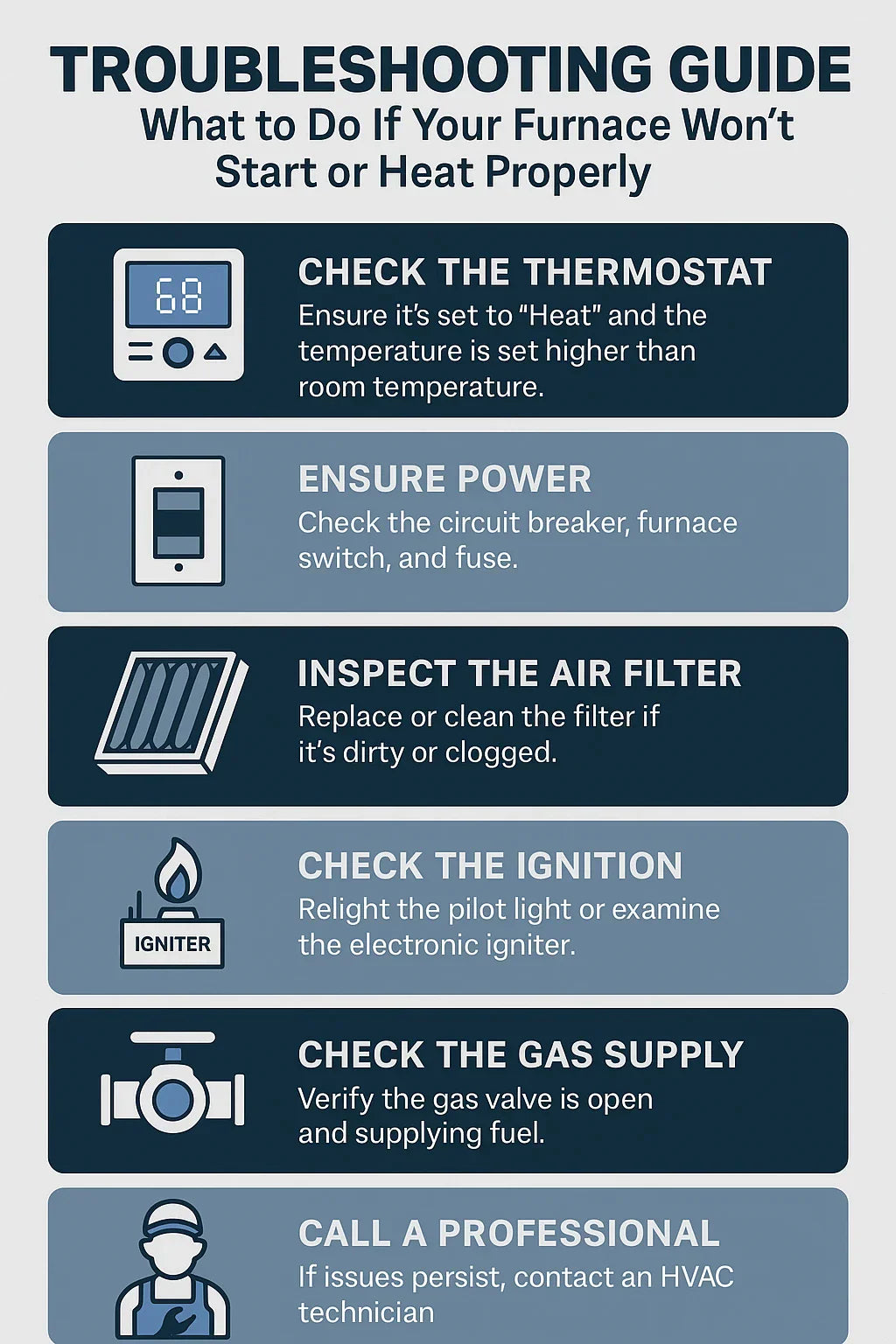
🔧 Troubleshooting Guide: What to Do If Your Furnace Won’t Start or Heat Properly
When your furnace won’t start or stops heating properly, it can quickly turn from a minor annoyance into a major problem—especially during the winter months. The good news? Many furnace issues are relatively simple to diagnose and fix, even for homeowners with little technical experience.
This guide will walk you through a step-by-step troubleshooting process, covering everything from thermostat misconfigurations to deeper mechanical and electrical failures. By the end, you’ll know when to attempt a DIY fix and when it’s time to call in a licensed HVAC professional.
🏠 Why Your Furnace Might Not Be Heating
Before diving into the troubleshooting steps, let’s break down the most common reasons your furnace isn’t working correctly.
-
Thermostat settings or power issues – Often the simplest culprit.
-
Dirty filters – Clogged filters restrict airflow and cause overheating shutdowns.
-
Pilot light or ignition problems – Gas furnaces need consistent ignition to burn fuel.
-
Tripped breakers or blown fuses – Electrical failures stop furnaces in their tracks.
-
Gas supply issues – No fuel = no heat.
-
Blocked vents or ducts – Poor airflow reduces heating efficiency.
-
Mechanical wear and tear – Motors, belts, and bearings fail over time.
-
Safety shut-offs – Modern furnaces have sensors that shut down when unsafe conditions are detected.
Understanding these categories will make troubleshooting much more systematic.
🕹️ Step 1: Check the Thermostat
Before assuming your furnace is broken, confirm that your thermostat is set correctly.
-
Ensure it’s set to “Heat” mode (not “Cool” or “Fan”).
-
Set the temperature at least 5 degrees higher than the current room temp.
-
If it runs on batteries, replace them.
-
For smart thermostats, check Wi-Fi connectivity and updates.
👉 Tip: Sometimes, thermostats get accidentally switched during seasonal transitions.
📖 Reference: Energy.gov – Thermostat Best Practices
🔌 Step 2: Verify Power Supply
If your furnace doesn’t start at all, it may not be getting power.
-
Check the breaker panel – Look for a tripped breaker and reset if necessary.
-
Inspect the power switch – Furnaces often have a light-switch-style toggle near the unit.
-
Confirm fuse status – Older systems may have inline fuses.
👉 If breakers trip repeatedly, it could indicate short-circuiting or a failing blower motor—call a pro.
📖 Reference: Family Handyman – Furnace Not Working?
🪣 Step 3: Inspect and Replace Air Filters
Dirty filters are among the top causes of furnace failure.
-
Remove the filter (located near the return duct or blower compartment).
-
If it’s gray, clogged, or older than 90 days, replace it.
-
High-MERV filters trap more particles but can also reduce airflow—stick to what your furnace manufacturer recommends.
👉 Keeping a clean filter can extend furnace life and lower utility bills.
📖 Reference: HVAC.com – How Often to Change Furnace Filters
🔥 Step 4: Check the Pilot Light or Ignition System
For older gas furnaces with a pilot light:
-
Open the access panel and look for a steady blue flame.
-
If it’s out, follow your manufacturer’s instructions to relight it.
-
If it won’t stay lit, the thermocouple may be faulty.
For modern electronic ignition systems:
-
Listen for clicking sounds (spark ignition) or look for glowing (hot surface igniter).
-
If ignition fails, components may need replacement.
👉 Never attempt ignition repairs if you smell gas—leave immediately and call your utility company.
📖 Reference: Home Depot – How to Light a Pilot Light
⛽ Step 5: Ensure Gas Supply Is Flowing
If your furnace is gas-powered but won’t heat:
-
Confirm your gas valve is fully open.
-
Check if other gas appliances (like a stove) are working.
-
In winter, ensure outdoor meters and regulators aren’t iced over or blocked by snow.
👉 If you suspect a gas leak (rotten egg smell), shut off the gas immediately and call your gas company.
📖 Reference: National Grid – What to Do If You Smell Gas
🌬️ Step 6: Inspect Vents and Airflow
Blocked airflow can make your furnace overheat and shut down.
-
Walk around your home and make sure supply and return vents are open and unobstructed.
-
Check for closed dampers in ductwork.
-
Outside, inspect intake and exhaust pipes for debris, leaves, or ice.
👉 A furnace that cycles on and off rapidly often points to airflow restrictions.
⚙️ Step 7: Look for Error Codes
Most modern furnaces have LED diagnostic lights.
-
Open the front panel and look for flashing lights.
-
Count the blinks and compare them with your owner’s manual.
-
Common codes point to ignition failures, pressure switches, or flame sensors.
👉 This built-in self-diagnosis feature can save you hours of guessing.
🧹 Step 8: Clean the Flame Sensor
A dirty flame sensor is a very common cause of furnace shutdowns.
-
Turn off power and gas.
-
Locate the thin metal rod near the burner assembly.
-
Remove and gently clean it with fine-grit sandpaper.
-
Reinstall and restart the furnace.
👉 If cleaning doesn’t help, replace the flame sensor (usually inexpensive).
🔊 Step 9: Listen for Unusual Noises
Strange sounds often reveal mechanical issues:
-
Squealing – Worn blower belt or motor bearings.
-
Banging/Thumping – Duct expansion or delayed ignition.
-
Clicking – Faulty relay or ignition.
-
Grinding – Blower motor failure.
👉 Loud or persistent noises usually require professional servicing.
🧰 Step 10: Advanced DIY Fixes (For Handy Homeowners)
If you’re comfortable with tools, you can attempt:
-
Replacing blower motor capacitors
-
Checking the draft inducer motor
-
Inspecting pressure switches with a multimeter
⚠️ Warning: Working inside the furnace cabinet involves high voltage and gas risks. If unsure, call a professional.
👷♂️ When to Call a Professional
Even the most seasoned DIYer should recognize when it’s time to get help. Call an HVAC technician if:
-
You smell gas.
-
Breakers keep tripping.
-
You hear loud bangs or grinding noises.
-
The furnace short cycles (starts and stops every few minutes).
-
There’s water pooling around the unit.
-
The heat exchanger may be cracked (carbon monoxide risk).
🛡️ Preventive Maintenance to Avoid Future Problems
The best troubleshooting is prevention. Follow these tips:
-
Change filters every 1–3 months.
-
Schedule annual HVAC tune-ups.
-
Keep furnace area clean and clear.
-
Test carbon monoxide detectors.
-
Seal duct leaks to reduce strain on the system.
📊 Cost Breakdown: DIY vs. Professional Repairs
| Problem | DIY Cost | Pro Repair Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Filter replacement | $10–$30 | $80–$150 |
| Flame sensor cleaning/replacement | $10–$50 | $150–$300 |
| Thermostat battery replacement | $5–$10 | $75–$125 |
| Blower motor replacement | N/A | $400–$1,200 |
| Ignition system repair | N/A | $300–$600 |
👉 In many cases, basic fixes save hundreds if caught early.
📌 Final Thoughts
When your furnace won’t start or heat properly, don’t panic—most issues are straightforward and fixable. Begin with simple checks like the thermostat, power, and filters before moving on to more complex components like ignition systems and flame sensors.
With regular preventive maintenance and timely repairs, your furnace can last 15–20 years or more. But if you notice persistent problems, rising repair bills, or safety hazards, it may be time to consider a furnace replacement instead of constant fixes.
In the next topic we will know more about: Will a Goodman 60,000 BTU Furnace Work with Smart Thermostats?