A Deep Sustainability Dive Into High-Efficiency Furnaces & Smarter Home Heating
🌱 Introduction: Welcome to the New Era of Low-Carbon Heating
If you ask Savvy what truly makes a modern home feel sustainable, she won’t point to solar panels, or insulation upgrades, or even high-SEER ACs. She’ll smile and say:
“The real sustainability magic starts in the combustion chamber.”
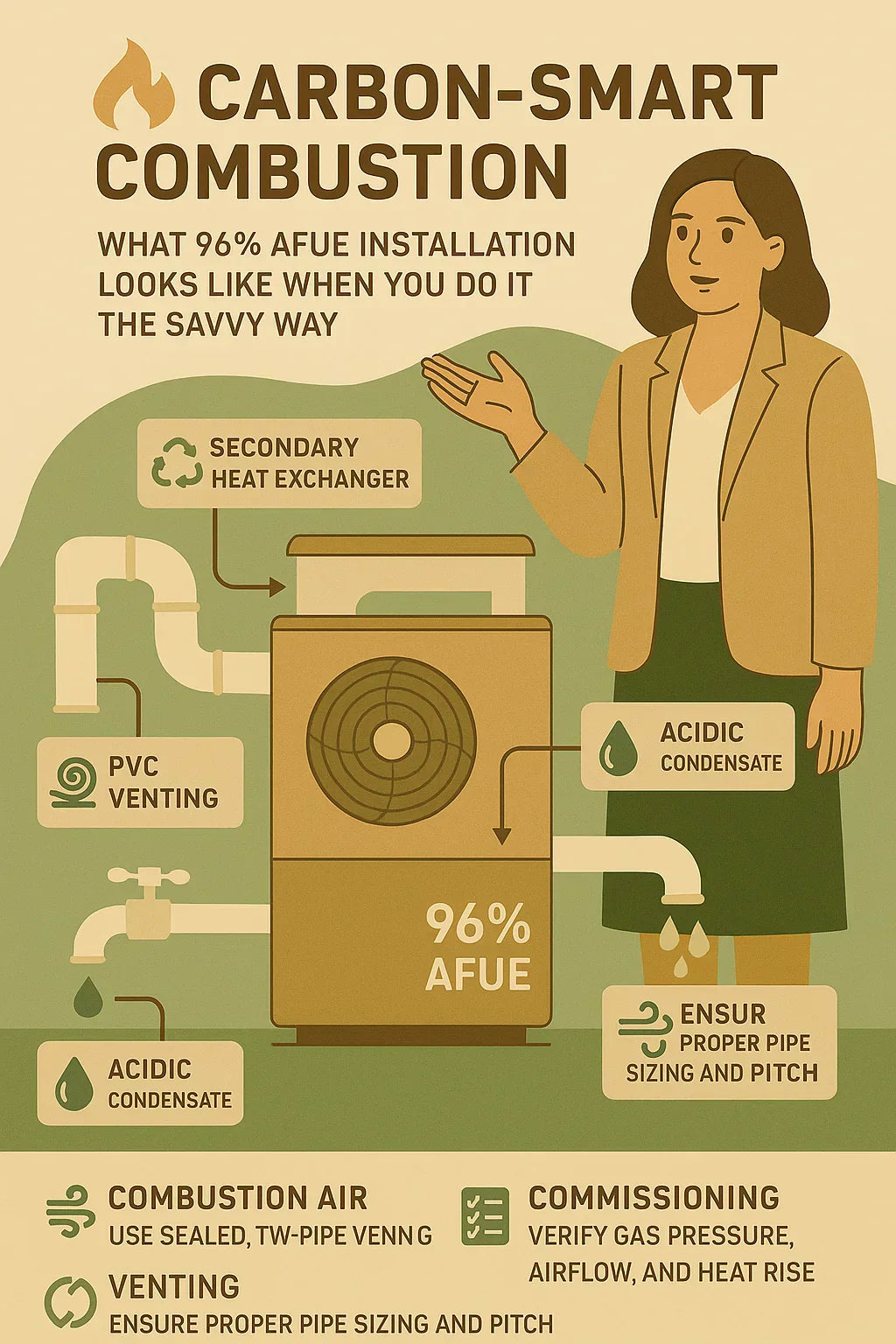
A 96% AFUE natural gas furnace — like the Goodman GR9S960804CN — is a marvel of engineering. For every dollar of fuel it consumes, 96 cents are transformed into usable heat. But here’s the understood secret among high-performance installers:
Efficiency ratings aren’t guaranteed. They must be earned through flawless installation.
A poorly installed 96% furnace can perform like an 80% unit, waste fuel, increase carbon emissions, and shorten its lifespan. But a Savvy-style installation transforms it into a carbon-smart comfort ecosystem — whisper-quiet, low-waste, and beautifully tuned to the home.
This guide takes you inside the world of environment-first furnace installation, step by step.
🔧 1. What Makes a Furnace 96% AFUE? The Sustainability Physics Behind It
Icon: ♻️
To understand carbon-smart installation, you first need to understand what makes a high-efficiency furnace so special.
🔥 The Secondary Heat Exchanger (The Carbon Saver)
Unlike standard furnaces that waste exhaust heat, a 96% AFUE condensing furnace extracts heat twice:
-
In the primary heat exchanger
-
Again in the secondary (condensing) heat exchanger
This second phase recovers latent heat from water vapor in the exhaust gases — reducing flue temperatures from 300–500°F down to about 100°F.
This dramatically lowers fuel waste and carbon output.
💨 PVC Venting (Because the Exhaust Is Cool Enough)
Since combustion gases are now cooler, they can be safely vented outdoors using PVC instead of metal flue pipe, reducing material costs and simplifying installation.
💧 Condensate Production (A Sign of Efficiency)
Condensing furnaces produce acidic condensate — a byproduct of advanced heat recovery. This must be drained responsibly, ideally using:
-
A condensate pump
-
A neutralizer cartridge
-
Proper downward pitch
Installing these correctly is a crucial sustainability practice.
🏡 2. Combustion Air Planning — The First Step of Carbon-Smart Installation
Icon: 🌬️
Your furnace needs oxygen just like you do. But where it gets that oxygen determines how efficient — and how sustainable — the system becomes.
🔍 Two Types of Combustion Air Configurations
1. Open Combustion (Uses Indoor Air)
Not ideal for tightly sealed modern homes because:
-
It depressurizes the home
-
It increases infiltration
-
It wastes conditioned air
-
It reduces efficiency
Think of it as borrowing heat from the space you're trying to heat.
2. Sealed Combustion (Uses Outdoor Air)
This is the Savvy-approved method.
A 96% AFUE furnace should always use two-pipe, sealed combustion:
-
One pipe brings in fresh outdoor air
-
One pipe exhausts combustion gases
🌎 Why Sealed Combustion Boosts Sustainability
-
No indoor air is wasted in the combustion process
-
Reduces drafts and infiltration
-
Improves indoor air quality
-
Allows the furnace to run efficiently in tight homes
-
Reduces carbon output through cleaner, more stable combustion
Verified Resource
EPA Indoor Air Quality Basics
🔗 https://www.epa.gov/indoor-air-quality-iaq
🧪 3. Venting Geometry — Where Efficiency Is Won or Lost
Icon: ➿
High-efficiency furnaces require venting systems that follow strict rules. Deviate from them even slightly, and efficiency plummets.
🔄 Savvy’s Venting Rules for a 96% Furnace
1. Maintain Proper Pipe Pitch
-
Exhaust (vent) pipe: ¼ inch per foot upward to the outdoors
-
Intake pipe: neutral or slightly sloped back toward the furnace
This prevents condensate pooling — a major cause of corrosion and performance loss.
2. Keep Pipe Lengths Within Manufacturer Limits
Every elbow and every foot of pipe adds resistance. Too much, and the pressure switch may fail, leading to shutdowns or short-cycling.
3. Use Smooth, Long-Radius Elbows
Short-radius elbows increase turbulence, raising static pressure and energy use.
4. Keep Intake and Exhaust Terminations Properly Spaced
They must never be too close or face each other — recirculating exhaust back into the intake is catastrophic for efficiency and safety.
Verified Resource
ASHRAE Ventilation Standards
🔗 https://www.ashrae.org
🧯 4. Gas Line Sizing — The Foundation of Clean Combustion
Icon: 🛢️
Your furnace can’t perform sustainably if it’s starving for natural gas. Most combustion inefficiency — and carbon waste — comes from undersized or poorly routed gas lines.
🔥 Savvy-Approved Gas Piping Guidelines
-
Use the correct pipe diameter (often ¾" or 1")
-
Follow the longest-run method for sizing
-
Limit unnecessary elbows
-
Install a sediment trap (dirt leg) to protect the burners
-
Test all joints with leak-detection fluid
-
Confirm manifold pressure with a manometer
Why It Matters
Incorrect fuel pressure leads to:
-
Dirty combustion
-
Higher CO emissions
-
Decreased AFUE in real-world operation
-
Shorter heat exchanger life
-
Increased gas consumption
Verified Resource
EnergyStar HVAC Installation Best Practices
🔗 https://www.energystar.gov
🌡️ 5. Heat Rise — The Most Commonly Ignored Sustainability Metric
Icon: 🌡️
Heat rise is the temperature difference between the air entering and leaving the furnace.
This one number tells you almost everything about whether the furnace is installed with carbon-smart precision.
📏 Target Heat Rise
Most 96% AFUE furnaces target a heat rise of:
35°F–65°F
If heat rise is too high:
-
Furnace overheats
-
Heat exchanger lifespan drops
-
Efficiency decreases
-
Fuel waste increases
If heat rise is too low:
-
Condensate forms where it shouldn’t
-
Efficiency plummets
-
Blower speed may be too high
-
Comfort suffers
Savvy’s Rule
Tune blower speed first. Burn cleaner, not harder.
🌀 6. Ductwork Compatibility — Your Furnace Can Only Be as Efficient as the Airflow You Give It
Icon: 🔁
This is where most 96% furnace installations fail.
A high-efficiency furnace is designed for high-volume, low-restriction airflow. If ductwork is too small or too restrictive, the whole sustainability promise collapses.
🛠️ Savvy’s Duct Rules
Supply + Return Must Provide 1200–1400 CFM
(Higher AFUE systems often target slightly higher airflow.)
Static Pressure Should Stay Below 0.5 inches WC
High static pressure = wasted energy + noisy operation.
Returns Matter More Than Supplies
Most homes have undersized returns, causing the blower to waste electricity pushing air through bottlenecks.
Verified Resource
ACCA Manual D (Duct Design Standard)
🔗 https://www.acca.org
💧 7. Condensate Management — The Forgotten Sustainability Battleground
Icon: 💧
Condensing furnaces remove so much heat from exhaust gases that they produce up to several gallons of acidic condensate per day.
If managed poorly, this can:
-
Damage drains
-
Corrode metals
-
Pollute soil
-
Reduce furnace efficiency
Savvy-Approved Best Practices
1. Install a Condensate Neutralizer
Raises the pH to protect plumbing and the environment.
2. Use Proper Traps & Vents
Prevent sewer gases from entering the home.
3. Provide Pump Redundancy Where Needed
Condensate pump failures are a high-risk, low-cost problem.
4. Use Rigid Tubing Where Possible
Flexible tubing kinks easily and interrupts drainage.
🧭 8. Commissioning — The Carbon-Smart Checklist That Separates Amateurs from Professionals
Icon: 📋
A 96% furnace is not “installed” — it is commissioned.
A carbon-smart commissioning process includes:
Instruments Used
-
Manometer
-
Combustion analyzer
-
Temperature probes
-
Static pressure gauge
-
Anemometer
Tests Performed
🔥 Combustion Testing
-
O₂ levels
-
CO ppm
-
CO₂ percentage
-
Flue temperature
💨 Airflow Testing
-
Total external static pressure
-
Return vs. supply balance
-
CFM measurement
🌡️ Temperature Split
Verifies heat rise and blower speed settings.
🧪 Gas Pressure Verification
Ensures clean, efficient combustion.
If any one of these metrics is off, carbon efficiency suffers.
🌍 9. Real-World Sustainability Gains — How a Savvy Installation Changes Everything
Icon: 🌎
A carbon-smart installation can reduce your household footprint dramatically.
🌟 Benefits
1. Lower Fuel Consumption
A perfectly tuned 96% furnace can save hundreds of dollars annually — and thousands of cubic feet of natural gas.
2. Lower Carbon Emissions
Every bit of wasted fuel becomes excess carbon. Good tuning means clean, complete combustion.
3. Longer Equipment Lifespan
Balanced temperatures and proper airflow protect the heat exchanger — the heart of the system.
4. Quieter Operation
Better airflow = less blower strain = less fan noise.
5. Better Indoor Air Quality
Sealed combustion keeps pollutants outside where they belong.
6. Higher Comfort Consistency
A carbon-smart furnace eliminates temperature swings and maintains steady, even heat.
🌟 Closing Thoughts: Carbon-Smart Isn’t Just Efficient — It’s Transformational
A 96% AFUE furnace isn't just a heating appliance.
It’s a gateway to a lower-carbon home.
But only when installed thoughtfully, sustainably, and scientifically.
When you follow Savvy’s principles — sealed combustion, perfect vent geometry, balanced airflow, precise gas delivery, and meticulous commissioning — your furnace becomes:
-
A carbon reducer
-
A comfort stabilizer
-
A whisper-quiet companion
-
A long-term sustainability investment
This is carbon-smart combustion.
This is the future of heating.
And this is how you make your 96% AFUE system truly worth it.
Buy this on Amazon at: https://amzn.to/4hyDyKH
In the next topic we will know more about: The Hidden Art of Copper — Line Set Bending, Flare Quality & Leak Prevention for R-32/R-410A Systems