If you’ve ever opened your furnace or AC panel and seen thin thermostat wires connected to a transformer, you might wonder:
👉 Why do HVAC systems use 24 volts instead of the same 120V or 240V that powers everything else in the house?
The answer is simple: safety, reliability, and efficiency.
Goodman 120V to 24V Transformer 0130M00140S
I’m Mark, and as a DIY homeowner who’s replaced my fair share of transformers and thermostats, I’ve come to appreciate why the HVAC industry standardized on 24V low-voltage controls decades ago. In this guide, I’ll explain in plain English why 24V is the sweet spot for HVAC systems—and what that means for you as a homeowner.
🧾 Table of Contents
-
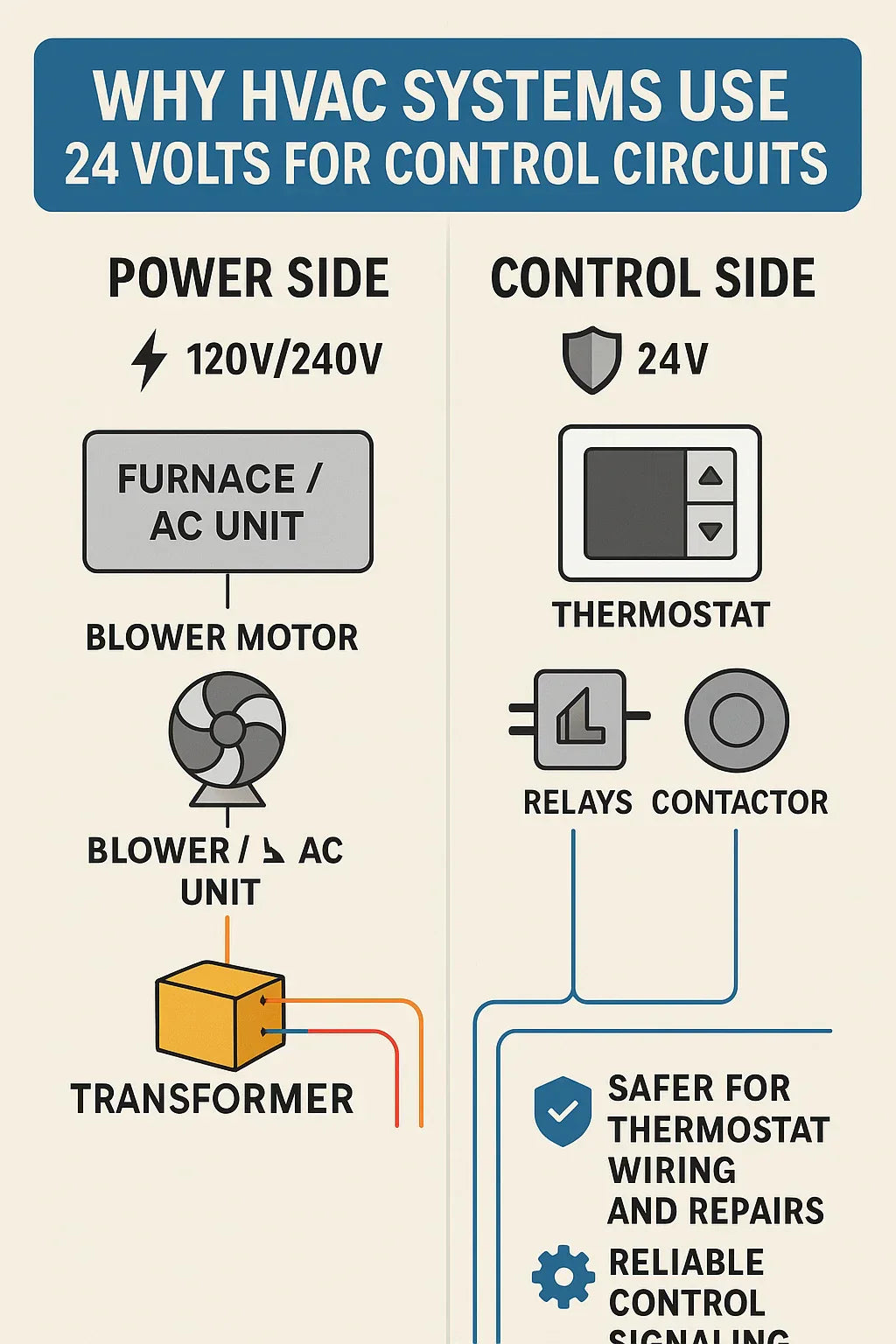
⚡ The Two Sides of HVAC Power
-
🛡 Why 24V Is Safer for Controls
-
🔍 Efficiency and Reliability Benefits of Low Voltage
-
🏠 The Thermostat: Your 24V Command Center
-
📜 A Short History of 24V in HVAC Systems
-
🧰 How Transformers Make 24V Work
-
⚖️ Why Not Use 12V, 48V, or 120V Instead?
-
📖 Mark’s Real-World Analogy (Light Switch Example)
-
🛡 Protecting Your 24V System (Fuses & Safety)
-
❓ FAQs About 24V Control Circuits
-
📚 Final Thoughts
⚡ 1. The Two Sides of HVAC Power
Your HVAC system runs on two types of electricity:
-
Line voltage (120V or 240V): Powers heavy equipment—compressors, blower motors, electric heating elements.
-
Low voltage (24V): Controls everything—thermostat, relays, contactors, safety switches.
Think of it like a factory:
-
Line voltage = machines doing the work.
-
Low voltage = supervisors giving commands.
👉 Technical breakdown: Electronics Tutorials – Transformer Basics
🛡 2. Why 24V Is Safer for Controls
The number one reason HVAC systems use 24 volts is safety.
-
Low shock risk: Unlike 120V or 240V, 24V is considered safe to touch under most conditions.
-
Thin wires allowed: 24V doesn’t require heavy insulation, so thermostat wires can be thin and flexible.
-
Safer DIY repairs: Homeowners can safely install or replace thermostats without risk of serious shock.
If thermostats carried 120V line power, replacing one would be as risky as wiring a breaker panel—not homeowner-friendly at all.
👉 Electrical safety reference: OSHA Electrical Standards
🔍 3. Efficiency and Reliability Benefits of Low Voltage
It’s not just safety—24V also makes HVAC systems more efficient and reliable.
-
Low energy consumption: 24V circuits draw very little power.
-
Long-distance signaling: Low voltage can travel across long thermostat wire runs without much loss.
-
Less wear: Relays and contactors triggered by 24V last longer than if they handled line voltage directly.
-
Compatibility: 24V works well with modern smart thermostats and accessories.
👉 Why low voltage is common in control systems: National Renewable Energy Lab – Low Voltage Applications
🏠 4. The Thermostat: Your 24V Command Center
Your thermostat doesn’t directly switch your furnace or AC on—it sends a 24V “signal” to the control circuits.
Typical thermostat wires:
-
R = 24V power
-
C = common (return path)
-
Y = cooling (compressor contactor)
-
W = heating (furnace relay)
-
G = fan
-
O/B = heat pump reversing valve
When you set your thermostat to “cool,” it simply connects the R (24V power) wire to the Y (cooling) wire. That 24V signal energizes a contactor coil in your outdoor AC, which then closes a 240V circuit to start the compressor.
So, your thermostat is like a messenger—it doesn’t do the heavy lifting, it just sends safe signals.
👉 Wiring explained: Family Handyman – Thermostat Wiring Guide
📜 5. A Short History of 24V in HVAC Systems
Why 24V specifically? Why not 12V or 48V?
-
Early thermostats: Mechanical mercury-switch thermostats in the mid-1900s were designed to work with 24V.
-
Industry standardization: HVAC manufacturers adopted 24V to ensure compatibility.
-
Balance of safety and reliability: High enough to trigger relays reliably, low enough to be safe.
Decades later, 24V remains the standard—keeping systems consistent across brands and generations.
👉 Historical HVAC background: ASHRAE – HVAC Systems and Equipment Handbook
🧰 6. How Transformers Make 24V Work
So how does your HVAC system get 24V from a 120V or 240V supply?
That’s the job of the transformer.
-
Primary side: Connects to 120V (U.S.) or 240V (some systems).
-
Secondary side: Outputs ~24V AC.
-
Capacity (VA): Usually 40VA, enough to run thermostat + relays.
If the transformer fails, your thermostat goes blank, and your system won’t run. That’s why transformer safety and compatibility matter.
👉 Testing guide: SFGate – How to Test a Furnace Transformer
⚖️ 7. Why Not Use 12V, 48V, or 120V Instead?
-
12V: Too low—long wire runs would have more voltage drop, and relays may not trigger reliably.
-
48V: Still safe but unnecessarily high for simple HVAC controls.
-
120V: Too dangerous for homeowners, requires heavy wires, and would wear out thermostats quickly.
👉 More on control system voltages: HVAC School – Common 24V Problems
📖 8. Mark’s Real-World Analogy (Light Switch Example)
Here’s how I explain it to friends:
Think of your thermostat like a light switch.
-
Instead of running dangerous 120V through the thermostat in your hallway, your system uses safe 24V wires to flip a bigger switch (contactor or relay) inside the furnace or AC unit.
-
The 24V control circuit acts as a messenger, telling the big, high-voltage components when to turn on or off.
Safer for you, safer for your equipment.
🛡 9. Protecting Your 24V System (Fuses & Safety)
Even though 24V is low voltage, it’s not immune to problems.
-
Inline fuses: Protect the transformer from shorts.
-
Proper wiring: Avoid pinched or bare thermostat wires.
-
Don’t overload: Adding too many accessories can exceed transformer VA rating.
-
Never bypass fuses: That’s how you fry control boards.
👉 Protection tips: Honeywell University – Transformer Sizing & Protection
❓ 10. FAQs About 24V Control Circuits
Q: Can an HVAC system run without 24V?
A: No—the thermostat and control relays depend on it.
Q: Do all thermostats use 24V?
A: Most wired ones do. Battery-only thermostats exist, but even they often need 24V for functions.
Q: Why not use batteries instead of 24V?
A: Batteries drain quickly, while 24V provides a continuous, reliable supply.
Q: How long should an HVAC transformer last?
A: 15–20 years under normal conditions.
📚 11. Final Thoughts
So, why does your HVAC system use 24 volts for control circuits?
Because 24V is the perfect balance of safety, reliability, and efficiency.
-
It keeps homeowners safe while letting thermostats send signals.
-
It reduces energy use and equipment wear.
-
It’s been the industry standard for decades, ensuring compatibility across systems.
As a homeowner, the key takeaway is this: respect the 120V side, but don’t be afraid of the 24V side. That’s the part designed to be safe and serviceable—even for DIYers like you and me.
In the next topic we will know more about: Should You Upgrade to a Higher VA Transformer? Pros, Cons & When It Makes Sense