When I was shopping for a new furnace, I kept running into the term Ultra-Low NOx. At first, I thought it was just another industry buzzword—like “premium efficiency” or “advanced comfort.” But after doing some digging, I realized it’s about a lot more than marketing.
👉 It’s about air quality, regulations, and compliance.
If you live in certain states like California, installing an Ultra-Low NOx furnace isn’t just a smart choice—it’s the law. And even if you don’t live in one of those areas, it’s worth understanding what NOx is, why it matters, and how a cleaner-burning furnace like the Goodman 80,000 BTU Ultra-Low NOx can benefit both your home and the environment.
🔬 What Is NOx?
NOx stands for nitrogen oxides, a group of gases released when fuels like natural gas, oil, or coal are burned.
Where NOx Comes From
-
🚗 Cars and trucks
-
⚡ Power plants
-
🔥 Residential and commercial furnaces
When natural gas burns, it combines nitrogen and oxygen at high temperatures, creating these gases.
Why It Matters
-
NOx reacts with other compounds in sunlight to create ground-level ozone, better known as smog.
-
It also contributes to acid rain and fine particle pollution.
-
Health effects include worsened asthma, bronchitis, and lung irritation.
👉 Tony’s Take:
“I always thought my old furnace just burned clean natural gas. I had no idea it was putting out pollution that affects air quality.”
The EPA explains NOx emissions here.
🌱 Environmental Impact
Reducing NOx is one of the fastest ways to improve local air quality.
NOx and Smog
-
In cities like Los Angeles, smog has been a health hazard for decades.
-
NOx is a key ingredient that makes smog worse when it reacts with volatile organic compounds (VOCs) under sunlight.
NOx and Health
-
According to the American Lung Association, NOx exposure can:
-
Increase asthma attacks
-
Cause coughing, wheezing, and difficulty breathing
-
Harm children’s lung development
-
NOx and Climate
-
While CO₂ gets most of the headlines, NOx also contributes indirectly to climate change by forming ozone, a potent greenhouse gas.
👉 Tony’s Perspective:
“I’m not a scientist, but when I found out NOx contributes to smog in my own community, it made me think twice. Breathing clean air matters to my family too.”
📜 Regulations You Should Know
Here’s where things get real: regulations around NOx emissions are getting stricter every year.
California: The Strictest Rules
-
The South Coast Air Quality Management District (SCAQMD) requires Ultra-Low NOx furnaces that emit less than 14 nanograms per joule (ng/J) of heat output.
-
These rules apply to Los Angeles, Orange, Riverside, and San Bernardino counties.
-
If you try to install a non-compliant furnace there, your permit can be denied, or you may face fines.
Other States Following
-
Nevada, Utah, and Arizona have started tightening NOx standards.
-
More states in the West are expected to follow California’s lead.
Federal Standards?
-
While there’s no nationwide Ultra-Low NOx requirement yet, the EPA and Department of Energy are actively studying it.
-
Many experts believe federal rules could be on the horizon.
👉 Tony’s Perspective:
“I didn’t want to buy a furnace that might be illegal in a few years. Spending a little extra now means I won’t get caught off guard by new rules later.”
South Coast AQMD rules explained here.
⚙️ How Ultra-Low NOx Furnaces Work
At first, I thought Ultra-Low NOx meant the furnace had less power. That’s not the case—it still puts out the same 80,000 BTUs. The difference is how it burns fuel.
Key Design Differences
-
Specially engineered burners: Mix gas and air more efficiently, reducing nitrogen formation.
-
Improved heat exchangers: Keep combustion temperatures in the optimal range to minimize emissions.
-
Sealed combustion: Keeps the burn cleaner and safer.
What You Notice as a Homeowner
-
Comfort: Same as a standard furnace.
-
Efficiency: My Goodman still runs at 80 AFUE, which means 80% of fuel turns into usable heat.
-
Noise: Often quieter because of updated burner technology.
👉 Tony’s Take:
“I honestly don’t feel any difference in how the furnace heats my house. The difference is in what’s coming out of the exhaust—it’s just cleaner.”
💰 Cost and Value
Here’s the question every homeowner asks: How much more does an Ultra-Low NOx furnace cost?
Upfront Costs
-
On average, Ultra-Low NOx furnaces cost $300–$800 more than standard low-NOx models.
-
That’s because of the specialized burners and certification process.
Long-Term Value
-
✅ Keeps you compliant with local laws (avoids fines or replacement costs).
-
✅ Helps improve local air quality.
-
✅ May qualify for rebates or incentives from your utility or state.
For example, some California utilities offer rebates of $200–$500 for installing an Ultra-Low NOx furnace.
👉 Tony’s Perspective:
“I paid a little more upfront, but it keeps me on the right side of the law. Plus, I feel better knowing my system pollutes less.”
Energy Star rebate finder is a great place to check incentives.
🛠️ Maintenance Notes
The good news is that Ultra-Low NOx furnaces don’t require exotic upkeep.
Standard Maintenance Applies
-
Change filters every 1–3 months.
-
Schedule annual inspections.
-
Keep vents and ducts clean.
Special Considerations
-
Because of the advanced burner design, a professional should handle any combustion adjustments.
-
Repairs may cost a little more if specialized parts are needed—but breakdowns are rare with proper care.
👉 Tony’s Take:
“I treat it just like any other furnace—keep the filters clean and get it checked once a year. No extra hassle.”
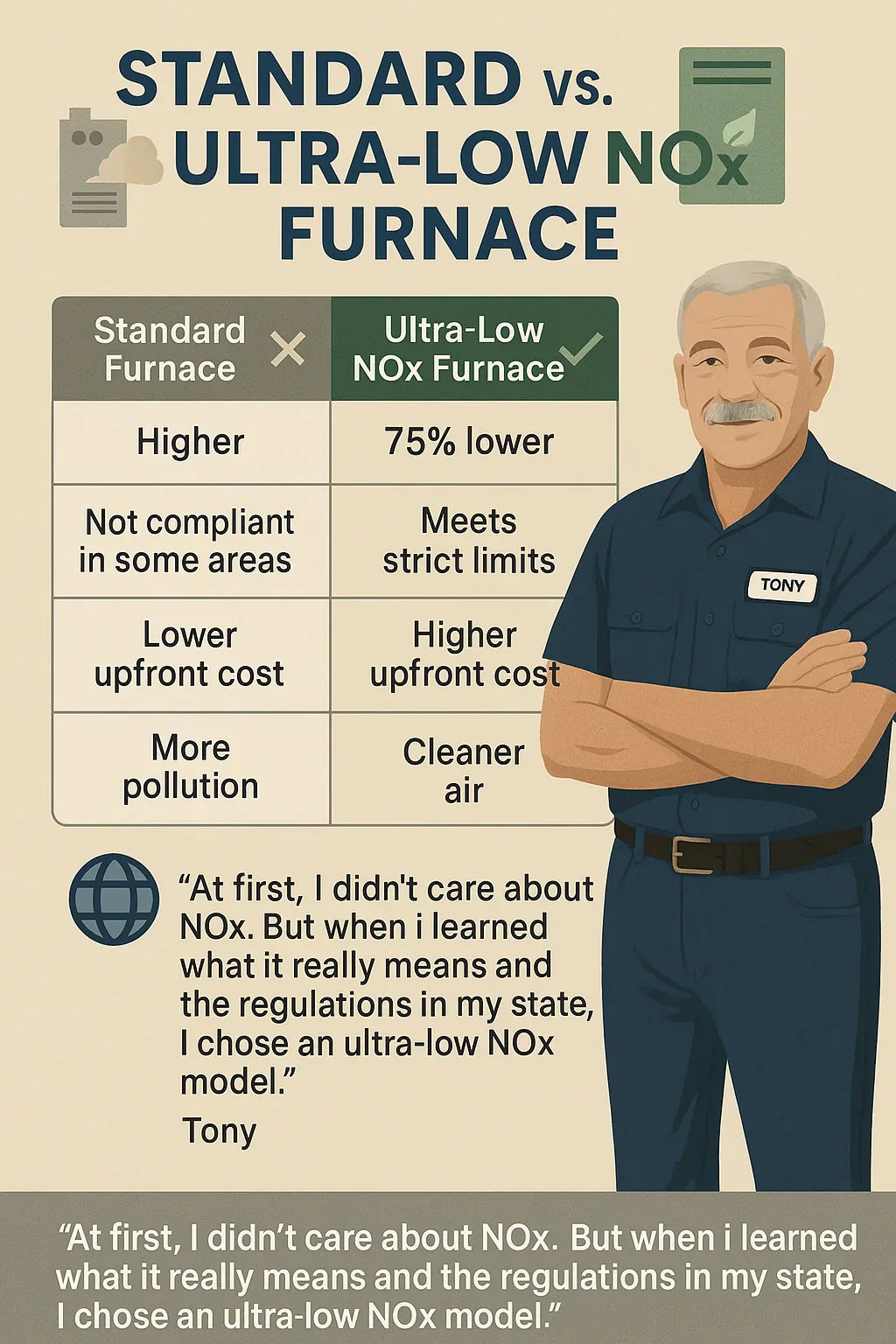
📊 Ultra-Low NOx vs. Standard Furnace Comparison
| Feature | Standard Furnace ❌ | Ultra-Low NOx Furnace ✅ |
|---|---|---|
| NOx Emissions | Higher | 75% lower (meets strictest rules) |
| Comfort | Normal | Normal (no difference) |
| Efficiency | 80%+ AFUE | 80%+ AFUE |
| Cost | Lower upfront | Slightly higher upfront |
| Legal Compliance | Not valid in CA/strict zones | Fully compliant |
| Rebates/Incentives | Limited | Often available |
| Environmental Impact | More pollution | Cleaner air, less smog |
🎯 Final Takeaway
An Ultra-Low NOx furnace isn’t about bells and whistles—it’s about cleaner air, healthier lungs, and staying compliant with regulations.
-
If you live in California or another regulated area, it’s not optional—it’s required.
-
Even outside those regions, it’s a smart move that future-proofs your home and helps cut down on pollution.
👉 Tony’s Advice:
“I didn’t buy my Ultra-Low NOx furnace just to follow the rules—I bought it because I want my kids and grandkids breathing cleaner air. If you can make your home comfortable and help the environment at the same time, that’s a win in my book.”
In the next topic we will know more about: Which Configuration Is Better for Your Home: Upflow or Horizontal Installation?