When you invest in a standby generator, you’re not just choosing the size or brand—you’re also choosing the fuel source that will keep your home running during an outage. And here’s the tricky part: your choice between natural gas (NG) and propane (LP) affects not only installation but also long-term costs, reliability, and convenience.
Generac Guardian® 70432 22kW Air-Cooled Standby Generator with Wi-Fi and Transfer Switch
If you’re wondering whether natural gas or propane makes more sense for your whole-house generator, this guide breaks it down step by step. By the end, you’ll know which fuel best fits your home, budget, and lifestyle.
⚡ Why Fuel Source Matters
Generators are engines, and like cars, they can’t run without fuel. Your choice of fuel impacts:
-
Operating costs (what you’ll pay during each outage).
-
Installation complexity (utility hookups vs. tank storage).
-
Reliability (how long you can run without refueling).
-
Power output (slight differences in wattage delivery).
-
Environmental footprint (emissions per hour of use).
👉 Picking the wrong fuel source could mean paying hundreds more per outage or being stuck in the dark when a storm lasts longer than expected.
🔗 Consumer Reports – Generator Basics
⛽ Natural Gas (NG) Overview
🔑 Key Benefits
-
Unlimited fuel supply: Tied directly into your utility’s natural gas pipeline.
-
Lower cost per hour: Typically cheaper than propane.
-
No storage tanks needed: Cleaner installation and less maintenance.
-
Hands-off convenience: You’ll never have to call for a refill truck.
⚠️ Potential Drawbacks
-
Utility dependent: If the gas utility is disrupted (rare but possible), your generator won’t run.
-
Slightly lower output: NG generators produce ~5–10% less power than the same unit on propane.
-
Gas meter upgrades: Some homes need a new meter to handle the generator’s demand.
Installation Requirements
-
Trenching to connect to the main utility line.
-
Utility inspection and approval.
-
May take longer to schedule if your gas company is backed up.
👉 Best for suburban and urban homeowners with reliable utility service.
🔗 U.S. Energy Information Administration – Natural Gas Basics
🛢️ Propane (LP) Overview
🔑 Key Benefits
-
Independent fuel supply: Stored in on-site tanks (250–500+ gallons).
-
Slightly higher output: Generators deliver more wattage on propane.
-
Reliable even if utilities fail: Works during gas line interruptions or earthquakes.
-
Long shelf life: Propane doesn’t degrade over time like gasoline or diesel.
⚠️ Potential Drawbacks
-
Higher fuel cost: Usually 2–3x the cost of natural gas per hour of runtime.
-
Refill logistics: Requires regular monitoring and propane deliveries.
-
Limited runtime: Your outage coverage depends on tank size.
Installation Requirements
-
Tank placement (above or below ground).
-
Regulator and safety shut-off valve setup.
-
Periodic tank inspections and refills.
👉 Best for rural homeowners without natural gas service—or those who want full control over their fuel supply.
🔗 Propane.com – Standby Generator Fuel Guide
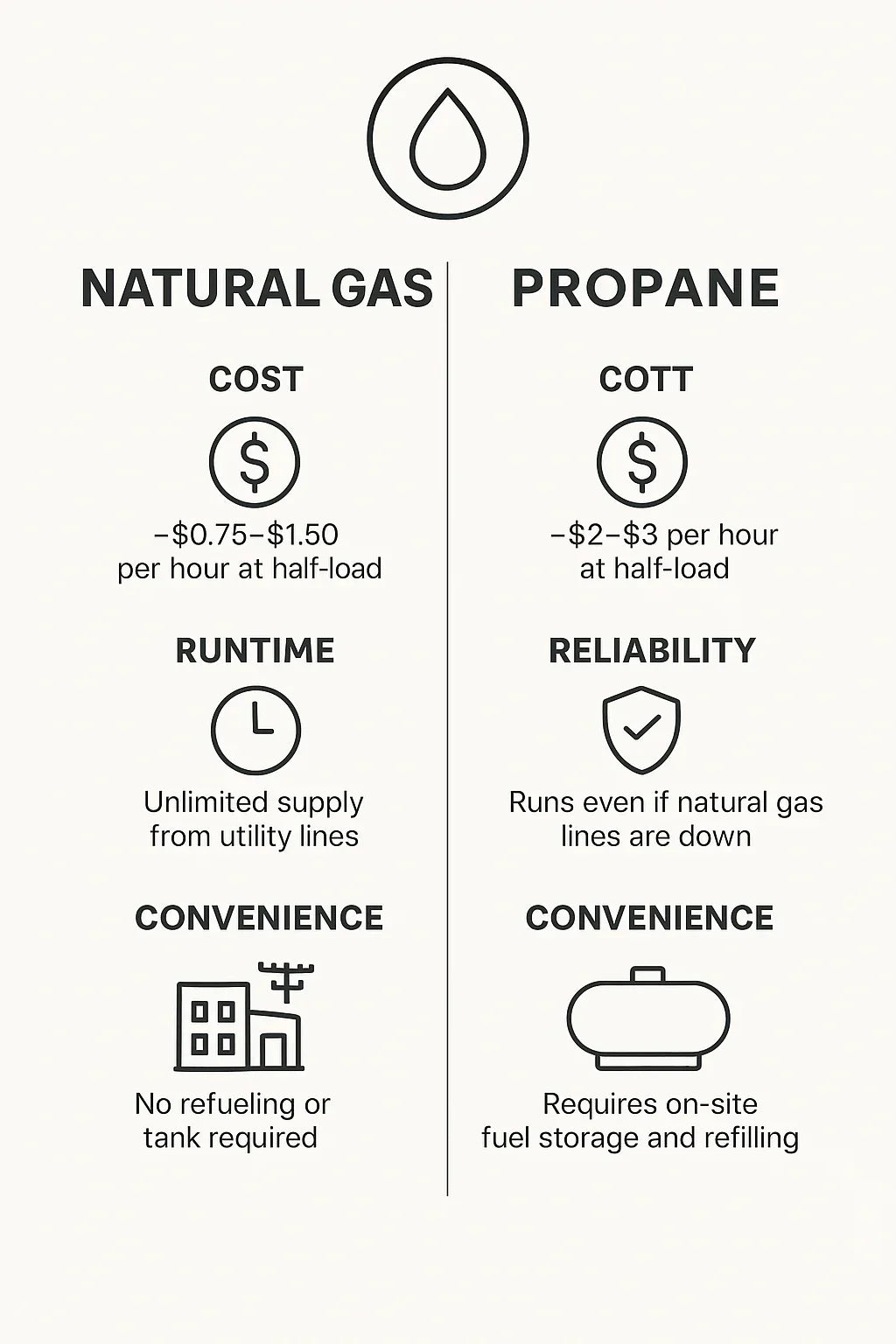
📊 Cost Comparison: Natural Gas vs. Propane
One of the biggest questions Savvy homeowners ask: “What will this cost me during an outage?”
Average Fuel Costs (2025 Estimates)
-
Natural Gas: ~$0.75–$1.50 per hour (half-load).
-
Propane: ~$2.00–$3.00 per hour (half-load).
Example: 22kW Generator During a 3-Day Outage (72 hours)
-
Natural Gas: ~$54–$108.
-
Propane: ~$144–$216 (plus tank refill, if needed).
👉 Over time, natural gas is far more economical, but propane gives independence from utilities.
🔗 Forbes – Whole House Generator Cost & Fuel Use
🔧 Installation & Maintenance Differences
Natural Gas Setup
-
Connects directly to utility lines.
-
Requires coordination with your gas provider.
-
May need a gas meter upgrade to handle extra demand.
Propane Setup
-
Requires an above- or below-ground tank.
-
Tanks must be installed with proper clearance and ventilation.
-
Requires regular monitoring and refills.
Maintenance
-
Natural Gas: Minimal extra maintenance (just generator servicing).
-
Propane: Tanks need periodic inspection and regulator checks.
👉 Installation costs for propane tend to be $500–$2,000 higher because of the tank and regulators.
🔗 Generator Installation Costs
❄️ Reliability & Outage Considerations
Natural Gas Reliability
-
Great for most suburban/urban homes.
-
Gas lines are rarely interrupted—but have been in earthquakes or major disasters.
Propane Reliability
-
Works even if utilities fail.
-
Limited only by tank size:
-
250-gallon tank: ~3–5 days of runtime.
-
500-gallon tank: ~7–10 days of runtime.
-
👉 Some homeowners install dual propane tanks to extend coverage.
🔗 Energy.gov – Backup Generator Options
🌍 Environmental Impact
Both NG and propane are cleaner than diesel or gasoline, but there are differences:
-
Natural Gas: Lower CO₂ per kWh than propane.
-
Propane: Lower carbon intensity per gallon, but less efficient.
-
Both produce fewer particulates and emissions than diesel.
👉 For eco-conscious homeowners, the difference between NG and propane is relatively small compared to the jump down to diesel or gasoline.
✅ Which Homeowners Should Choose Which?
Choose Natural Gas if:
-
You have NG service at your home.
-
You want lower operating costs during outages.
-
You prefer the convenience of unlimited runtime.
-
You don’t want the hassle of fuel deliveries.
Choose Propane if:
-
You live in a rural area without NG service.
-
You want energy independence from utilities.
-
You’re prepared to manage tank refills and inspections.
-
You want higher generator output from the same unit.
📈 Final Verdict: Best Fuel for a 22kW Generator
For most suburban and urban homeowners, natural gas is the practical and cost-effective choice. It offers unlimited runtime, lower costs, and set-it-and-forget-it convenience.
For rural or off-grid homeowners, propane makes more sense—even if it costs more—because it gives you full control over your fuel supply.
👉 The bottom line: Pick the fuel source that fits your location, budget, and tolerance for ongoing management.
In the next topic we will know more about: How Quiet Is the Generac Guardian 70432? Noise Levels Explained