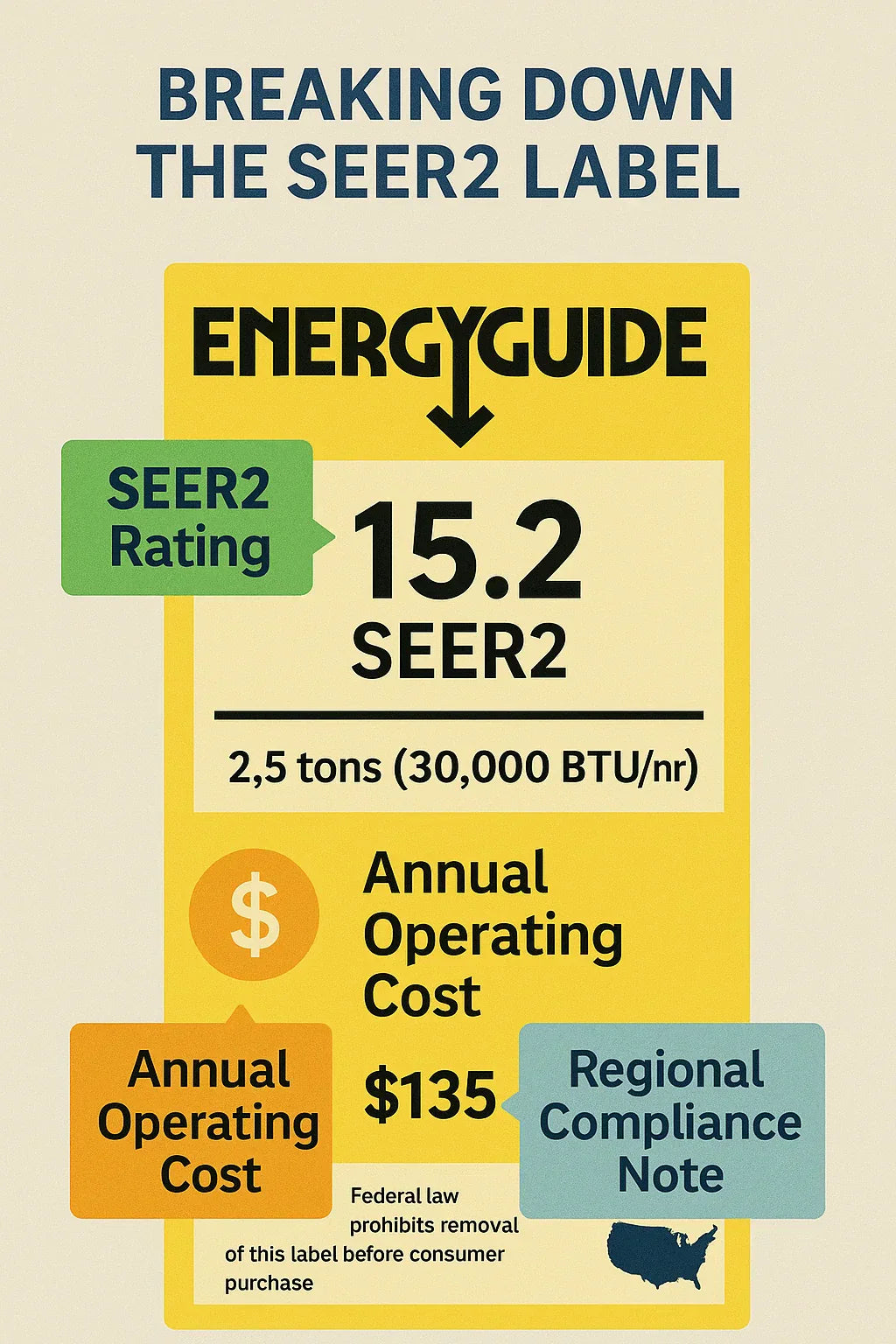
If you’ve ever shopped for a new air conditioner or heat pump, you’ve probably noticed the bright yellow EnergyGuide label or a manufacturer sticker attached to the unit. These labels look simple, but they carry crucial information about efficiency, costs, and compliance. With the rollout of SEER2 standards in 2023, knowing how to decode these labels is more important than ever.
In this guide, I’ll walk you through each part of a SEER2 rating label so you can make confident, cost-saving decisions for your home comfort system.
What Is a SEER2 Label?
A SEER2 label is a standardized tag required by federal regulations to help homeowners compare HVAC systems on an even playing field. The label includes the system’s efficiency rating, cooling capacity, estimated energy costs, and compliance with regional standards.
You’ll typically find SEER2 information in two places:
-
The yellow EnergyGuide label attached to the side of new equipment.
-
The manufacturer’s data sticker (usually inside the air handler panel or condenser casing).
These labels are designed to simplify shopping, but if you don’t know what to look for, you could easily misunderstand what the numbers mean—or worse, choose a system that isn’t the right fit for your home.
The Key Elements of a SEER2 Label
Understanding the SEER2 label starts with breaking it down into its main components.
Efficiency Rating (SEER2 Number)
The headline number on the label is the SEER2 rating. This is the Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio 2, which measures how efficiently the system cools your home over a typical season.
-
14.3 SEER2: The minimum rating in most U.S. regions starting in 2023.
-
15–17 SEER2: Mid-efficiency systems, often balancing cost and performance.
-
18+ SEER2: High-efficiency systems, often ENERGY STAR certified, with advanced inverter technology.
The higher the number, the less energy your system will use to deliver the same amount of cooling. But keep in mind—higher SEER2 doesn’t automatically mean it’s the best choice for your budget (we’ll cover that later).
Capacity and Cooling Output
Another important part of the label is the system’s cooling capacity, measured in tons or BTUs. This tells you how much cooling the unit can provide.
A mismatch between your home’s cooling needs and the system’s capacity can undo the benefits of a high SEER2 rating. For example, an oversized unit will cycle on and off too often, wasting energy and wearing down components faster.
Energy Use and Operating Cost Estimates
Most EnergyGuide labels also include an estimated annual operating cost. This number is based on national average electricity rates and assumes average usage.
Important note: Your actual costs can vary significantly depending on local utility rates, how well your home is insulated, and your climate zone. Think of this figure as a ballpark comparison, not a guaranteed bill.
Regional Compliance Notes
Since 2023, HVAC efficiency standards have been region-specific. For example, the South and Southwest regions have stricter minimums than the North. Some labels include compliance notes to help homeowners avoid buying a system that doesn’t meet local requirements.
If you’re unsure what the minimum standard is in your area, see the U.S. Department of Energy’s regional efficiency breakdown at energy.gov.
How to Compare Labels Between Models
When standing in a showroom or browsing online, you might be comparing two systems that both look good on paper. Here’s how to make sense of the labels:
-
Start with SEER2 rating: Higher means more efficient, but calculate whether the energy savings justify the higher upfront cost.
-
Check capacity: Make sure the BTU/ton rating matches your home’s needs (a Manual J calculation is the gold standard).
-
Look at operating cost estimates: Use these for relative comparison, not exact bills.
-
Factor in rebates and warranties: A system with a higher SEER2 might qualify for tax credits or utility rebates, making it more affordable in the long run.
For example, if you’re choosing between a 14.3 SEER2 and a 17 SEER2 unit, the label may show the 17 SEER2 system uses significantly less energy. If you live in a hot climate and run your AC often, those savings could add up quickly.
Common Misunderstandings When Reading SEER2 Labels
Even with standardized labels, there are a few traps homeowners fall into:
-
Confusing SEER with SEER2: Some equipment may still list the old SEER rating. Be sure you’re comparing SEER2, which reflects new testing standards.
-
Taking cost estimates as exact: The “annual cost” is based on averages, not your specific situation.
-
Believing higher SEER2 = always better: A 20 SEER2 system may not make sense if you live in a mild climate with low cooling needs.
For more clarity on efficiency ratings, the ENERGY STAR efficiency standards page at energystar.gov is a reliable resource.
Why Decoding SEER2 Labels Saves You Money
Taking the time to understand SEER2 labels pays off in several ways:
-
Avoid costly mistakes: Prevent overspending on a system that’s too large or not compliant in your region.
-
Maximize rebates and credits: Many programs require proof of efficiency rating. For example, Section 25C federal tax credits provide up to $2,000 for qualifying heat pumps. See the IRS tax credit details.
-
Lower lifetime costs: A correctly chosen SEER2-rated system will reduce your monthly bills for 10–15 years.
Organizations like the Air Conditioning Contractors of America (ACCA) and ASHRAE efficiency standards provide technical guidance, while the EPA energy efficiency and HVAC page explains how upgrades reduce environmental impact.
Final Thoughts from Alex Lane
SEER2 rating labels may look overwhelming at first glance, but once you know what each part means, they become a powerful tool for making smart decisions. Look beyond just the big number—consider capacity, operating cost, and whether the system fits your home’s actual needs.
If you’re still new to SEER2, I recommend starting with the full breakdown here: What is SEER2 and Why It Matters.
And if you’re wondering whether upgrading to a higher SEER2 system always makes sense, check out the next guide: Is a Higher SEER2 Rating Always Better? When It’s Not Worth the Upgrade.
Alex Lane
Your Home Comfort Advocate