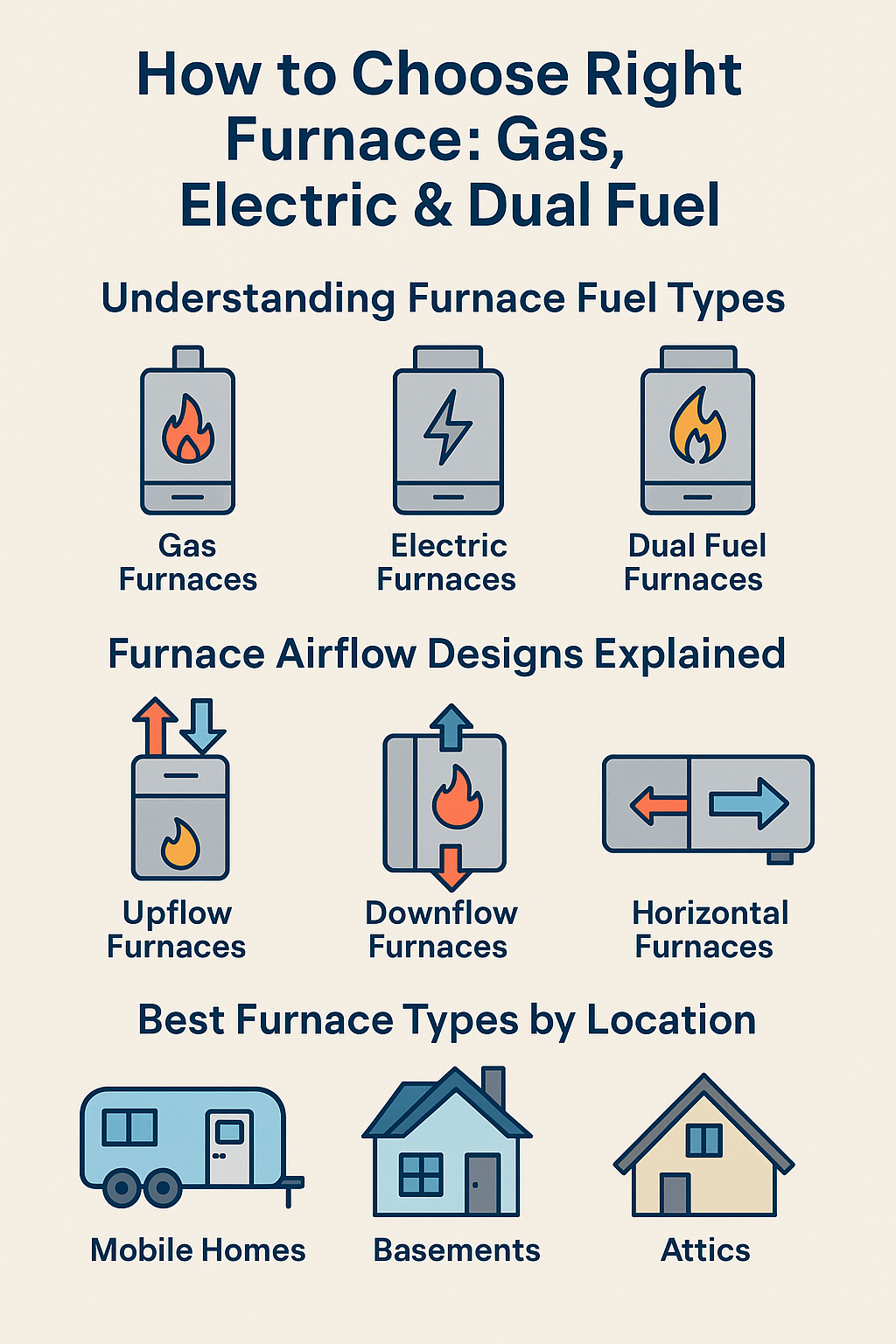
Looking to upgrade or replace your home heating system?
Choosing between a gas, electric, or dual‑fuel furnace can be tricky—especially if you're also trying to figure out which direction your furnace should flow (up, down, or sideways). This guide breaks down everything you need to know in plain language, with real-world advice to help you find what works best for your climate, budget, and space.
💡 What to Consider Before Choosing a Furnace
Before you compare fuel types or airflow configurations, ask yourself:
-
Do I have access to natural gas or only electricity?
-
What are my utility rates like?
-
Where will the furnace be installed—attic, basement, closet, crawl space?
-
Is efficiency or upfront cost more important right now?
-
How long do I plan to stay in this home?
If you're feeling overwhelmed already, don't worry—we’ll walk through it all.
🔌 Fuel Type Options: Gas vs. Electric vs. Dual-Fuel
Let’s start with the three main types of furnaces based on how they generate heat.
🔥 Gas Furnaces
Gas furnaces burn natural gas (or propane) to heat air and push it through your duct system.
Why choose gas?
It’s a great option in colder regions where gas is cheap and reliable. Modern high-efficiency models reach up to 98% AFUE.
Pros:
-
Strong heating output—great for freezing temps
-
Can save money long-term in areas with low gas prices
-
Tons of models available for any home size
Cons:
-
Requires a gas line and proper venting
-
Slightly more maintenance than electric
-
Needs a carbon monoxide detector for safety
➡️ Want to see how it compares? Check out our full breakdown of Fuel Types Explained
⚡ Electric Furnaces
Electric furnaces use resistance coils to heat air—no flame or combustion involved.
Why go electric?
If you don’t have access to natural gas or live in a milder climate, electric furnaces are clean, safe, and easy to install.
Pros:
-
No gas hookup or venting needed
-
Lower upfront cost
-
Quiet and low maintenance
Cons:
-
May cost more to run if electricity rates are high
-
Not the best for large homes in cold climates
-
Check out this electric furnace guide for more pros and cons
♻️ Dual-Fuel (Hybrid) Systems
This setup combines an electric heat pump with a gas furnace—automatically switching between them based on outdoor temps.
Why hybrid?
It’s designed for energy savings: the heat pump handles mild weather efficiently, and the gas furnace kicks in during freezing spells.
Pros:
-
Smart energy use based on climate
-
Lower operating cost long term
-
Often qualifies for rebates or incentives
Cons:
-
Higher initial investment
-
Slightly more complex installation
🌬️ Airflow Orientation: Upflow, Downflow, or Horizontal?
Even the best furnace won’t work properly if the airflow direction doesn’t match your home’s duct layout.
⬆️ Upflow Furnace
-
Pulls air in from the bottom and sends warm air up
-
Best for homes with basements or crawlspaces
-
Easier to service and install in vertical spaces
⬇️ Downflow Furnace
-
Takes air from the top, pushes heat downward
-
Great for attic installs or homes built on slabs
-
Compact and efficient for homes with lower ceilings
↔️ Horizontal Furnace
-
Moves air side to side, lying flat on its side
-
Perfect for mobile homes, crawl spaces, and tight attics
-
Space-saving choice with slightly higher install cost
👉 Haven’t seen our visual layout guide yet? Take a look at Upflow vs. Downflow vs. Horizontal
🏡 What Furnace Works Best in Each Type of Space?
Matching the right furnace to your installation space can save you serious headaches (and installation costs).
🚐 Mobile Homes
-
Airflow: Downflow or horizontal
-
Fuel: Electric or propane
-
Look for mobile-home-certified models
🏚️ Basements
-
Airflow: Upflow
-
Fuel: Gas, electric, or dual-fuel
-
Easy maintenance and install access
🏠 Attics
-
Airflow: Horizontal or downflow
-
Fuel: Electric (easiest venting), or sealed gas
-
Add a drip pan and insulation to prevent moisture issues
Curious which system fits your home? Here’s our full guide on Best Furnace Types for Special Spaces
💸 Cost & Efficiency Quick Guide
| Feature | Gas Furnace | Electric Furnace | Dual-Fuel System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Install Cost | $$$ | $$ | $$$$ |
| Monthly Bills | $ (if gas is cheap) | $$–$$$ | $ (optimized) |
| Efficiency Rating | 80–98% AFUE | 100% | 95–100%+ (varies) |
| Lifespan | 15–20 years | 20–30 years | ~20–25 years |
❓ FAQs: Choosing the Right Furnace
1. What's the most energy-efficient furnace?
Dual-fuel systems are the most efficient overall, especially in mixed climates.
2. Is a gas or electric furnace better for small homes?
Electric furnaces are great for small homes with limited space and mild weather.
3. Can I install a furnace in my attic?
Yes—just make sure it’s a horizontal or sealed-combustion downflow unit.
4. What’s the average lifespan of a furnace?
Electric: 20–30 years. Gas: 15–20 years. Dual-fuel: ~20–25 years.
5. Are rebates available for high-efficiency models?
Many utility companies offer rebates for ENERGY STAR® certified systems.
6. What’s better: high AFUE or low upfront cost?
If you’ll stay in your home long term, go for the high AFUE—it pays off over time.
🛒 Ready to Start Shopping?
Browse high-efficiency gas, electric, and dual-fuel furnaces for any space at
👉 The Furnace Outlet
Need help finding the right fit? Drop us a message—we’re happy to help.
🔗 Internal Link Navigation
-
➡️ Next: Best Furnace Type for Mobile Homes, Basements & Attics