Introduction: The Cost of Inefficient Cooling 🌱
Heating and cooling your home accounts for a significant portion of household energy use, often up to 50% of electricity bills in the summer months. For eco-conscious homeowners like Savvy, inefficient cooling not only drives up costs but also increases your carbon footprint.
Making smart air conditioning choices — from selecting the right system to maintaining it properly — can dramatically improve energy efficiency, reduce bills, and support sustainability goals. In this guide, we’ll dive deep into practical strategies for energy-efficient cooling, emphasizing modern eco-friendly systems like the Goodman 3-Ton R-32 air conditioner.
Step 1: Selecting the Right Air Conditioning System 🏡
Choosing the correct system for your home is the foundation of energy efficiency.
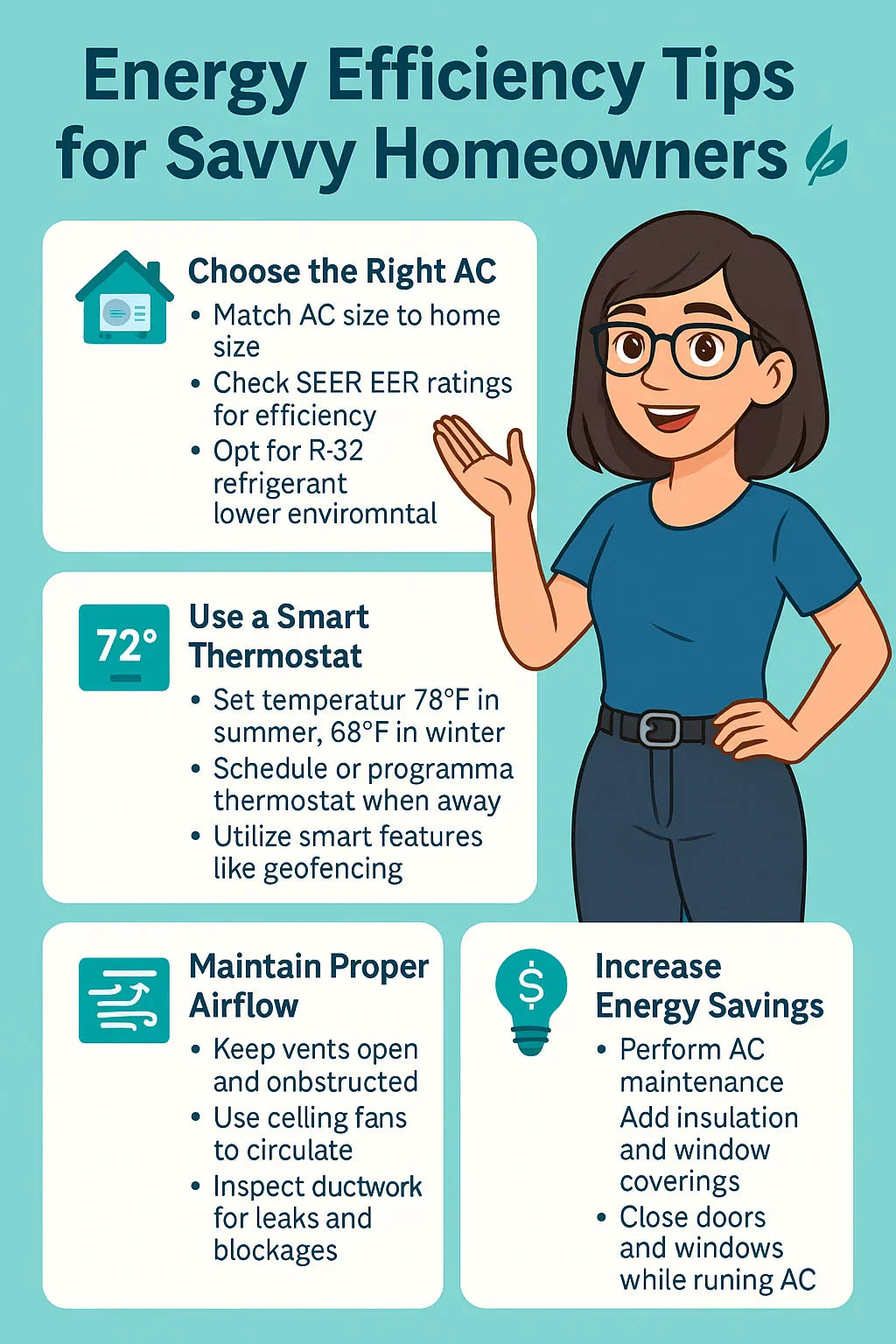
1. Match AC Size to Your Home
-
A system that is too small will overwork, increasing energy use.
-
An oversized system cools too quickly, causing short cycling, reducing efficiency.
-
For medium-sized homes (1,500–1,800 sq ft), a 3-Ton unit like the Goodman R-32 is ideal.
2. Understand SEER and EER Ratings
-
SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio): Higher SEER = more efficient cooling
-
EER (Energy Efficiency Ratio): Measures efficiency at a specific temperature
-
Modern R-32 units often outperform traditional R-410A systems in both metrics
3. The Benefits of R-32 Refrigerant 🌿
-
Lower Global Warming Potential (GWP) than R-410A
-
Superior energy efficiency
-
Future-compliant refrigerant reducing environmental impact
External Reference:
Step 2: Smart Thermostat Usage 🌡️
Thermostats are not just temperature controllers — they are key tools for energy savings.
1. Optimal Temperature Settings
-
Summer: 78°F (25.5°C) for occupied rooms
-
Winter: 68–70°F (20–21°C) for occupied spaces
-
Increase temperature a few degrees when away to reduce energy use
2. Programmable and Smart Thermostats
-
Set schedules for occupancy and peak energy hours
-
Use geofencing features to adjust cooling based on home presence
-
Track energy usage to identify wasteful habits
3. Avoid Extreme Adjustments
-
Rapidly lowering or raising temperatures increases energy use and stresses the AC system
External Reference:
Step 3: Proper Airflow and Ventilation 🌬️
Airflow significantly impacts energy efficiency.
1. Keep Vents and Registers Clear
-
Blocked vents reduce airflow, causing the system to work harder
-
Clean grilles regularly to remove dust and debris
2. Use Ceiling Fans to Aid Distribution
-
Fans circulate cooled air, allowing thermostat to be set a few degrees higher
-
Reduces compressor runtime and energy consumption
3. Inspect and Maintain Ductwork
-
Leaks can waste up to 30% of cooled air
-
Seal and insulate ducts to optimize energy use and airflow
External Reference:
Step 4: Regular Maintenance 🛠️
Maintenance ensures your system remains efficient and long-lasting.
1. Filter Care
-
Inspect monthly and replace every 1–3 months
-
Prevents airflow restrictions and keeps indoor air quality high
2. Clean Coils and Fins
-
Dirty evaporator or condenser coils reduce heat transfer efficiency
-
Straighten bent fins to maintain airflow
3. Check Refrigerant Levels
-
Low refrigerant causes system inefficiency
-
Certified HVAC technicians can safely check and recharge R-32
4. Annual Professional Tune-Up
-
Inspect electrical components, compressors, and fans
-
Verify proper operation and optimize energy performance
External Reference:
Step 5: Home Insulation and Energy-Saving Upgrades 🏠
Efficient cooling isn’t only about the AC — your home’s structure matters:
1. Seal Windows and Doors
-
Prevents cooled air from escaping
-
Reduces strain on the AC
2. Upgrade Insulation
-
Proper insulation in walls, attic, and floors minimizes heat gain
-
Keeps indoor temperatures stable
3. Energy-Efficient Window Treatments
-
Reflective blinds, curtains, or solar shades reduce solar heat gain
4. Reflective or Green Roofing
-
Reduces roof surface temperature, lowering AC workload
External Reference:
Step 6: Behavioral Tips for Energy Savings 💡
Small daily habits can yield substantial savings:
-
Close doors and windows while cooling
-
Limit heat-generating appliances during peak hours
-
Use programmable timers for AC and fans
-
Monitor energy consumption using smart meters or apps
Step 7: Savvy’s Recommendations for Sustainable Comfort 🌎
Combining system choice, maintenance, insulation, and smart usage creates maximum energy efficiency:
-
Select R-32 ACs – Lower GWP, better efficiency
-
Maintain the System – Clean filters, coils, and ducts
-
Use Smart Thermostats – Reduce waste and optimize runtime
-
Optimize Home Envelope – Insulation, window treatments, and reflective surfaces
-
Monitor Usage – Adjust behavior for energy-conscious operation
Step 8: Real-World Energy Savings Examples 🏡
Example 1:
A 3-Ton R-32 AC in a 1,700 sq ft home reduced electricity use by 12% in the first year compared to the previous R-410A system.
Example 2:
With proper thermostat scheduling, a homeowner saved 15% annually, maintaining consistent comfort and lower carbon emissions.
Step 9: Long-Term Benefits of Energy Efficiency 🌱
-
Lower Energy Bills – Immediate financial benefit
-
Reduced Carbon Footprint – Supports sustainability goals
-
Extended Equipment Life – Less stress on components
-
Reliable Comfort – Stable indoor temperatures year-round
Conclusion: Lower Bills and a Greener Home ✅
Energy efficiency in home cooling is achievable by:
-
Choosing the right AC system (like the Goodman 3-Ton R-32)
-
Maintaining proper airflow and system care
-
Using smart thermostats and energy-conscious habits
-
Improving home insulation and shading
By integrating these strategies, homeowners achieve comfort, savings, and sustainability — the three pillars of Savvy living.
In the next topic we will know more about: Is the Goodman 3-Ton R-32 Air Conditioner a Good Fit for Your Home? Zoning, Layout, and Sizing Tips