Alex Lane here — your Home Comfort Advocate.
Let’s get right to it: you’re choosing between a gas and an electric furnace, and everyone’s throwing numbers at you.
“Gas is cheaper!”
“Electric is more efficient!”
“AFUE says this one’s better!”
But what does energy efficiency really mean for your monthly bills — and which furnace type actually saves more over time?
In this guide, we’re going beyond the spec sheet to compare gas and electric furnace efficiency in real-world conditions: how they perform in different climates, how fuel and power impact savings, and which system delivers the best return on your energy use.
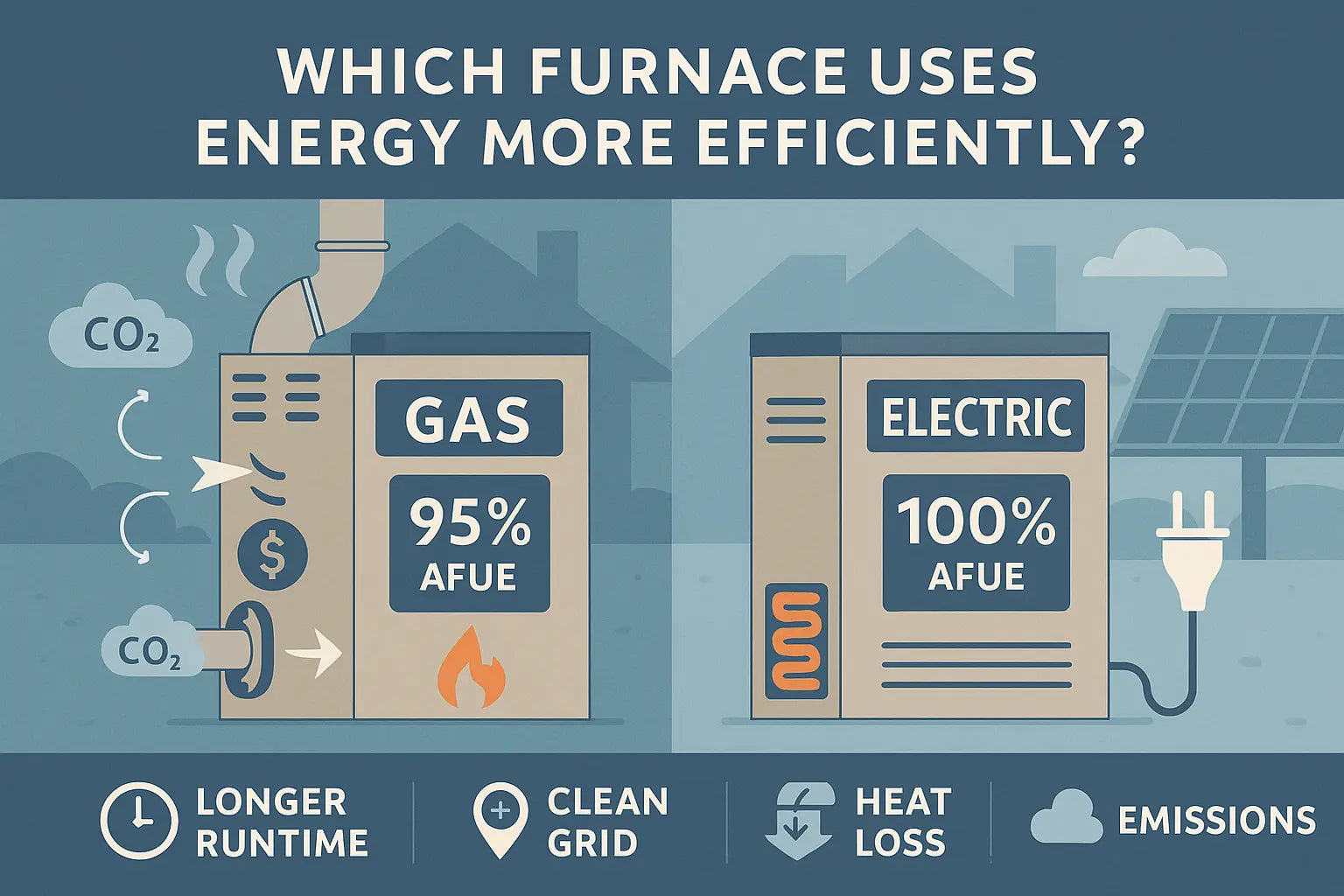
What Is AFUE — and Why It’s Only Half the Story
AFUE stands for Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency. It tells you how much of the fuel a furnace uses is actually converted into usable heat. The higher the AFUE, the less energy is wasted.
-
Gas furnaces typically range from 80% to 98% AFUE
-
Electric furnaces usually hit 95% to 100% — with no flue losses
So on paper, electric wins — right?
Not so fast.
AFUE doesn’t account for:
-
How much your fuel costs
-
How long your furnace runs
-
Heat loss through ductwork or insulation
-
Emissions or grid energy source
It’s a great starting point — but not the full picture. Carrier does a solid job explaining how AFUE ratings are calculated and why they matter.
Where Efficiency Is Lost: Real-World Performance Factors
A furnace might be 95% efficient in a lab, but your home isn’t a lab. Here’s what reduces actual efficiency:
🔥 Combustion & Venting (Gas Systems)
-
Heat escapes through the flue/exhaust
-
Combustion process creates unavoidable energy loss
-
Older gas systems often lack sealed combustion
⚡ Grid Losses (Electric Systems)
-
Electric heat is 100% efficient at the source
-
But if your electricity comes from coal or natural gas plants, up to 60% of energy may be lost before it reaches your home
-
It’s all about your grid mix (we’ll get to that below)
🌬️ Duct Losses
-
Both furnace types can lose 20–30% of heat through leaky or poorly insulated ductwork
-
Energy.gov offers a great breakdown of how duct sealing and insulation affect system efficiency
Climate Counts: Runtime Efficiency in Action
Let’s look at two homes — same size, different climates:
🏠 Home A: Michigan (Cold Climate)
-
Gas furnace heats faster, cycles less often
-
Electric furnace runs longer, drawing more expensive energy
-
Result: Gas is more efficient and cheaper to operate
🏠 Home B: North Carolina (Mild Climate)
-
Electric furnace maintains steady temps without heavy use
-
Gas furnace doesn’t get to show off its rapid heat output
-
Result: Electric is more efficient for low-demand heating
Climate-driven runtime and seasonal usage patterns play a major role in overall system efficiency. The EIA’s Residential Energy Consumption Reports provide excellent regional data showing how heating needs — and fuel usage — vary across the country.
Emissions & “True” Efficiency: Is Electric Really Cleaner?
There’s a big reason many homeowners are switching to electric: environmental impact.
Electric furnaces don’t emit carbon monoxide or burn fuel in your home — but that doesn’t mean they’re carbon-free.
🔌 Electric Furnaces
-
100% efficient at converting electricity to heat
-
Emissions depend on where your electricity comes from
-
In clean-grid states like Vermont or Washington, they’re nearly zero-emission
-
In coal-heavy states, they can be worse than gas in terms of carbon output
🔥 Gas Furnaces
-
More efficient at generating heat per dollar
-
Still release CO₂ — even high-efficiency units
Want to check your state’s grid? The EPA’s eGRID database shows electricity emissions by source across the U.S.
Energy Efficiency by Use Case
| Scenario | Winner | Why |
|---|---|---|
| Cold climate, older home | Gas furnace | Faster heat, better runtime |
| Mild climate, modern build | Electric furnace | Clean, steady efficiency |
| Off-grid solar or clean utility | Electric furnace | Pairs well with renewables |
| High gas prices, limited insulation | Depends | May need hybrid or heat pump |
Efficiency depends on your home, climate, and energy mix. That’s why I always say: don’t shop by rating alone — shop by fit.
Don't Forget: Insulation, Sizing & Ducts Matter Too
Even the most efficient furnace can underperform in a leaky home. To get the most out of your system:
-
Seal your ducts (especially in attics and crawlspaces)
-
Upgrade insulation and weather stripping
-
Size your furnace correctly — too large and it short-cycles, too small and it runs constantly
Small upgrades here can improve efficiency by 10–30% without touching your equipment. Energy.gov offers DIY guidance for homeowners looking to plug the gaps.
So, Which Furnace Type Saves More?
Here’s my bottom-line advice:
✅ Go Gas If:
-
You live in a cold climate
-
You have a gas hookup
-
You want short-term energy savings and fast heating
✅ Go Electric If:
-
You live in a mild climate
-
You’re investing in solar or grid electrification
-
You want low maintenance and potentially cleaner operation
Remember, AFUE is one piece of the puzzle — but total efficiency depends on your home, your grid, and your goals.
Want the Full Comparison?
Check out our complete guide:
👉 Gas vs. Electric Furnaces: Which Is Better? for performance, costs, and long-term value breakdowns.
Next up: 👉 Safety and Maintenance: What to Know About Gas vs. Electric Furnaces — where we look at what it takes to keep each system running safely and reliably.
Alex Lane
Your Home Comfort Advocate