Energy costs are steadily climbing, and savvy homeowners are feeling the pinch. If you're considering a PTAC system like the GE Zoneline 15,000 BTU PTAC Heat Pump (Model AZHS15DCXXA), one of your biggest concerns is likely: how much will it cost to run?
To get a clear picture of potential savings, you need to understand two key efficiency metrics: EER (Energy Efficiency Ratio) and CEER (Combined Energy Efficiency Ratio). In this guide, we’ll break down these terms, explain how they apply to the GE Zoneline, and help you estimate how much this unit could save you each year.
🔢 What Is EER and Why Does It Matter?
EER stands for Energy Efficiency Ratio. It measures how efficiently an air conditioning system can cool a space. Specifically, it is calculated as:
EER = BTUs of cooling output / watts of electrical input
This measurement is usually taken under set conditions: 95°F outdoor temperature, 80°F indoor temperature, and 50% relative humidity.
The GE Zoneline's EER
-
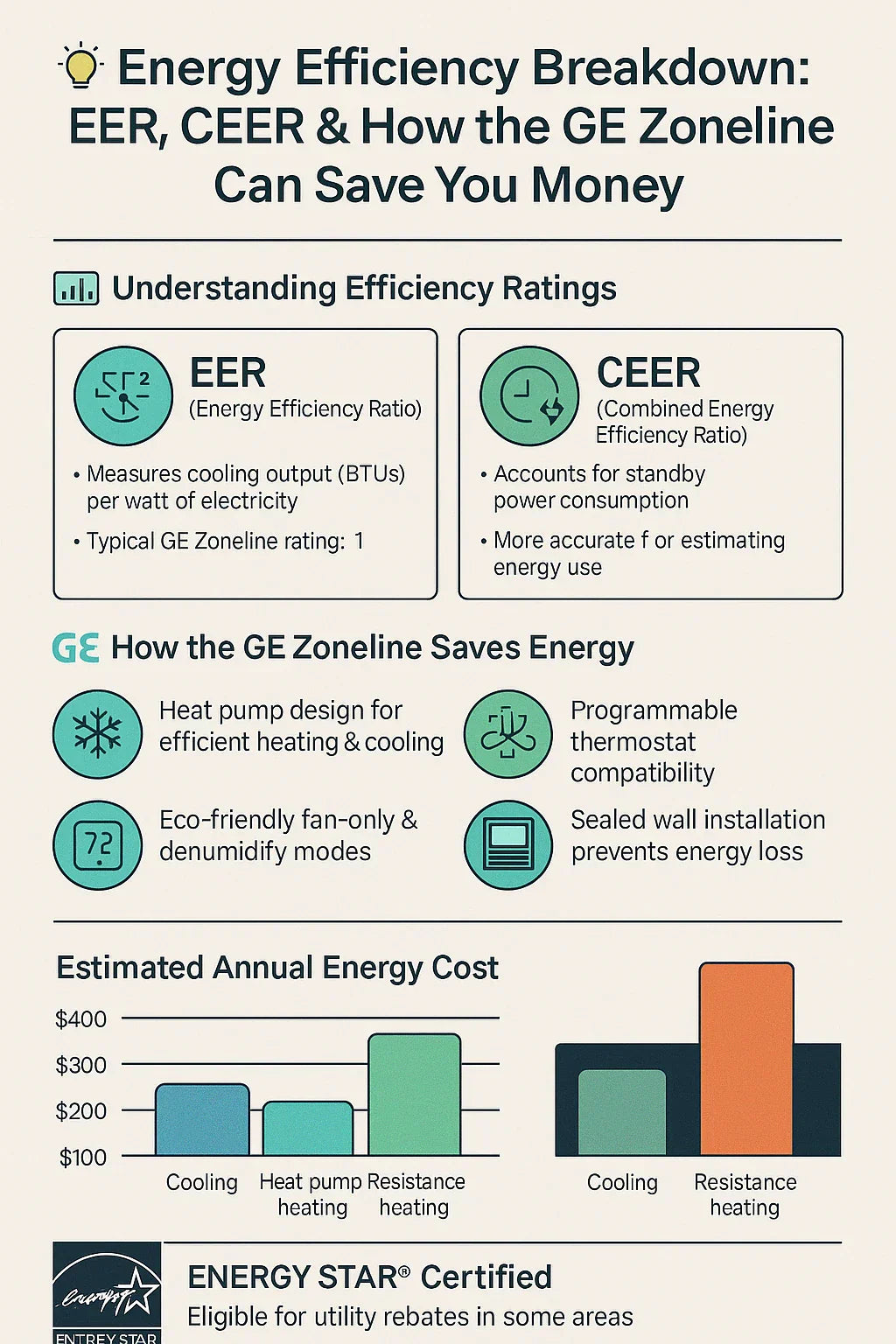
Rated EER: ~11.0 (varies slightly by model)
-
This means it produces 11 BTUs of cooling for every watt of energy consumed
-
Anything above 10.0 is considered efficient for PTAC units
🔄 What Is CEER and How Does It Differ from EER?
CEER, or Combined Energy Efficiency Ratio, is a newer and more comprehensive standard introduced by the Department of Energy.
CEER Includes:
-
The energy used during active cooling (like EER)
-
Standby and off-mode power consumption
This gives a more accurate picture of how efficient the unit is in real-world usage across an entire season.
-
CEER is often 5–15% lower than EER
-
For the GE Zoneline, CEER varies depending on settings and thermostat configuration but is still competitive among PTACs
🚀 How the GE Zoneline Improves Energy Efficiency
The Zoneline isn't just efficient on paper—it incorporates several real-world energy-saving features.
⚡ Heat Pump Technology
-
Provides heating with less electricity than electric resistance
-
Ideal for climates where winter temps stay above freezing
🔡 Programmable & Auto Fan Modes
-
Reduces unnecessary fan cycling
-
Auto mode adjusts fan speed based on room temperature
🌡️ Built-In Dehumidification
-
Cools while removing moisture without dropping temp excessively
-
Prevents overcooling (a common waste of energy)
📅 Occupancy-Based Energy Management
-
Compatible with thermostats that detect when a room is vacant
-
Perfect for guest suites, Airbnb rooms, and hotels
💸 Real-World Energy Cost Estimates
Let’s run a scenario for a home using the Zoneline in a 750 sq. ft. space in a moderate climate.
🌬️ Summer Cooling Example
-
Cooling BTU: 15,000
-
EER: 11.0
-
Energy Use per Hour: ~1.36 kW
-
6 hours/day x 120 days/year = 816 hours
-
Annual kWh Use: ~1,110
-
U.S. average electric rate: $0.16/kWh
-
Annual cooling cost: ~$177
♨️ Winter Heating Example (Heat Pump)
-
Heat pumps are ~300% efficient vs. resistance heat
-
Compared to electric baseboards: saves ~$0.10–$0.20 per heating hour
-
Over 1,000 heating hours = $100–$200+ in heating savings
🌍 Climate Zone Impacts on Efficiency
Where you live greatly affects how much you’ll benefit from GE Zoneline’s features.
| Region | Summer Intensity | Winter Severity | Efficiency Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Florida/Texas | High | Mild | Excellent efficiency all year |
| California/Oregon | Moderate | Mild | Highly efficient year-round |
| Minnesota/Maine | Moderate | Very Cold | Cooling efficient; backup heat needed in winter |
💼 Energy Rebates & Incentives
Many local utilities and state energy programs offer rebates on:
-
Energy Star PTACs
-
Programmable Thermostats
-
Heat pump installations
GE Zoneline units often qualify depending on your state.
🛠️ Maintenance = Efficiency Preservation
Keeping your PTAC running efficiently year after year requires simple, regular maintenance:
-
Clean filters monthly (dirty filters force fan motors to work harder)
-
Inspect drain pans and condensate lines for clogs
-
Vacuum coil fins annually to prevent dust buildup
-
Use a surge protector to prevent energy loss from voltage drops
✅ Pros and Cons of GE Zoneline Efficiency
| Pros | Cons |
| High EER/CEER | Not as efficient as mini splits |
| Heat pump reduces winter costs | Backup heat draws more power in cold climates |
| Programmable & eco modes | Requires proper installation for full efficiency |
| Qualifies for rebates | Slightly higher upfront cost than non-Energy Star PTACs |
📆 Final Verdict: Can the GE Zoneline Save You Money?
Yes, especially when installed in the right climate and used year-round.
With:
-
Competitive EER (11.0) and CEER ratings
-
Dual-mode cooling + heat pump operation
-
Smart thermostat and occupancy control compatibility
...the GE Zoneline delivers real-world energy savings for spaces between 500–800 sq. ft.
In moderate climates, it can act as your primary comfort system, and over the course of a year, may save you $150–$400 compared to older units or resistance-only heating.
Need help estimating your real energy savings with the GE Zoneline in your zip code? Send us your climate zone and room size—we’ll help you run the numbers!
In the next topic we will know more about: Maintenance Tips to Keep Your GE Zoneline Running Like New